coding standard guidelines
git
What is code readability and how to improve it
Did you know that in 1999, NASA's Mars Climate Orbiter was destroyed due to a software bug caused by low code readability, costing $320 million?
Having readable code is probably one of the top priorities for companies these days; it's so remarkable that, without knowing it, when you improve readability, you are also applying almost every other metric about coding standards and guidelines in the industry.
🤯 "Any fool can write code that a computer can understand. Good programmers write code that humans can understand." - Martin Fowler
Code readability refers to how easily any person can understand the purpose, structure, and operation of a piece of code. Code that is easy to read and understand is more maintainable, easier to modify or update, and less likely to contain errors or bugs.
🤯 "Code is read much more often than it is written." - Guido van Rossum (creator of Python)
Low readability costs a lot of money
Poor code readability can lead to several problems that can cost a company money:
Increased debugging time: If code is difficult to read and understand, it can take longer to identify and fix bugs, which can increase the amount of time and resources needed to debug the code. This can lead to increased project costs and delays.
Difficulty maintaining code: If code is difficult to read and understand, it can be difficult for new developers to make changes or updates to the code. This can lead to increased development costs and delays as developers spend more time trying to understand the code.
Increased risk of errors: If code is difficult to read and understand, it is more likely that errors or bugs will be introduced as the code is modified or updated. These errors can cause the program to malfunction, leading to lost productivity and potentially lost revenue.
Tips you can follow to improve the code readability
In this lesson, we will go over a few tips you can follow to improve the readability of your code.
Choose variable names wisely
Where do I start? This is one of the most difficult tasks in coding.
- Choose descriptive and meaningful names.
- Limit the use of most abbreviations or acronyms.
- Use variable naming conventions like "camelCase" or "snake_case".
- Avoid using single-letter names.
- Keep names short, but not too short; concise, but still descriptive.

Split your code into smaller functions
Instead of nesting blocks of code, consider refactoring the code into smaller functions and calling those functions at the appropriate times. This can reduce the overall depth of nesting in your code.

Avoid using the else statement
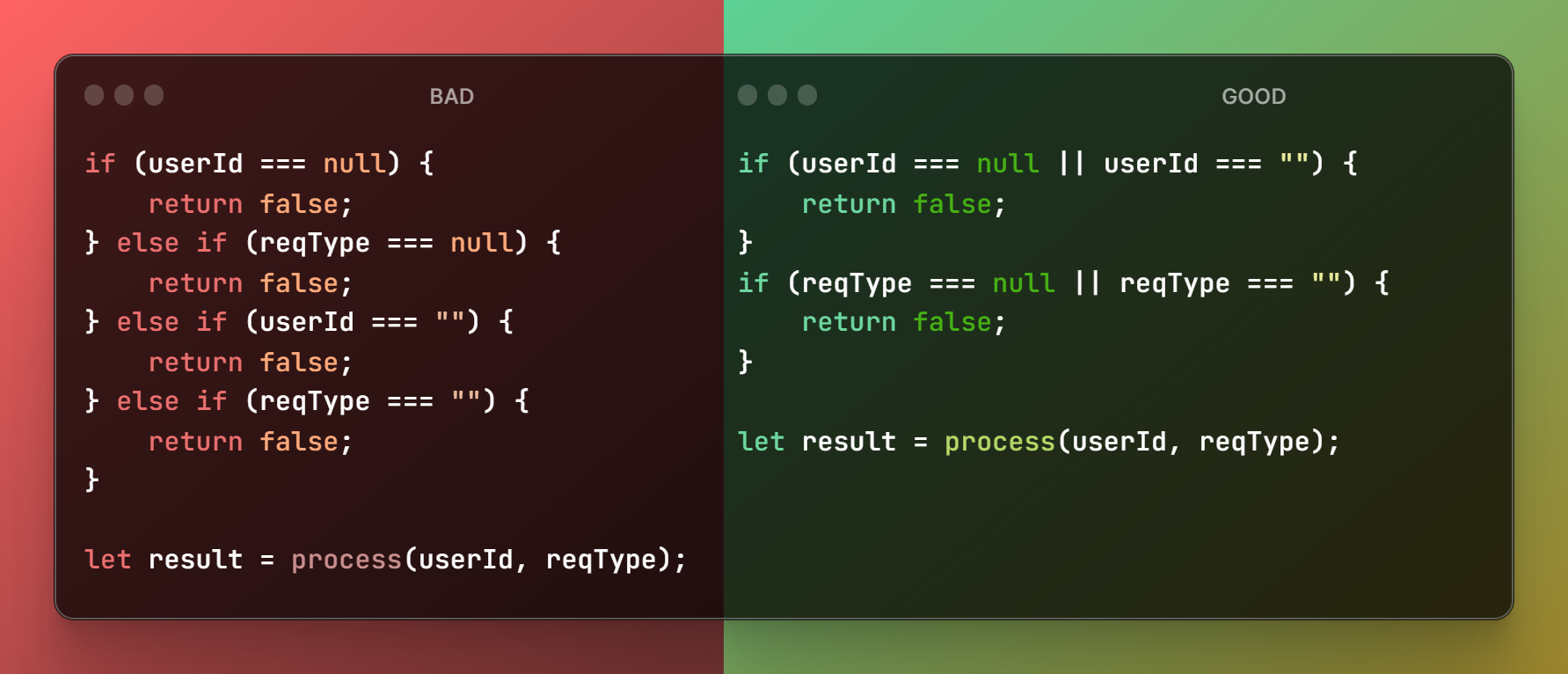
Careful with indentation
Of course, indentation is a vital part of readability.
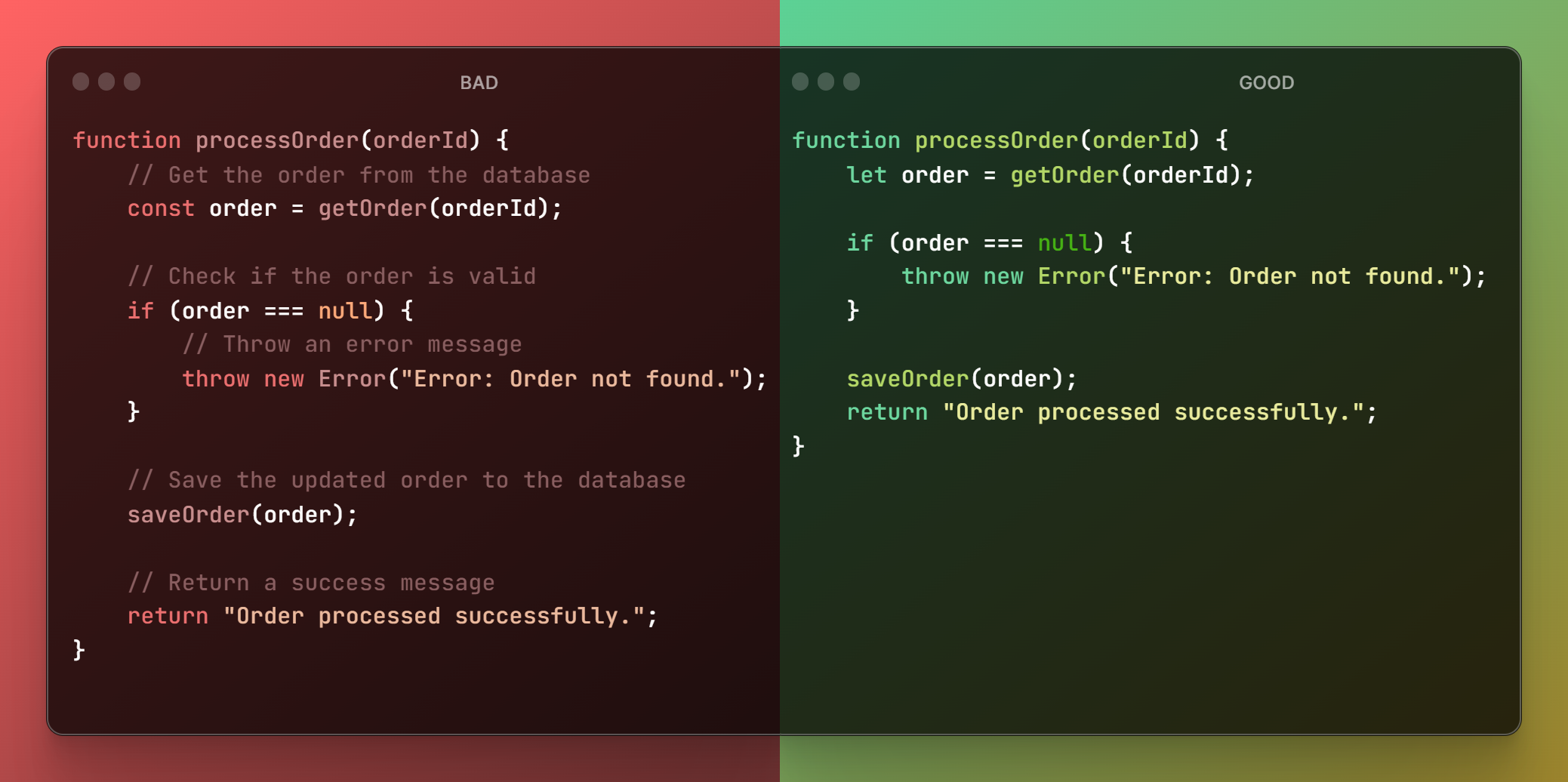
You don't need that many comments
When you are about to add a comment, think for a second: Do I need this comment? Can I increase readability if I avoid it?
99% of the time, there is no need for comments if your code has good readability and follows best practices.
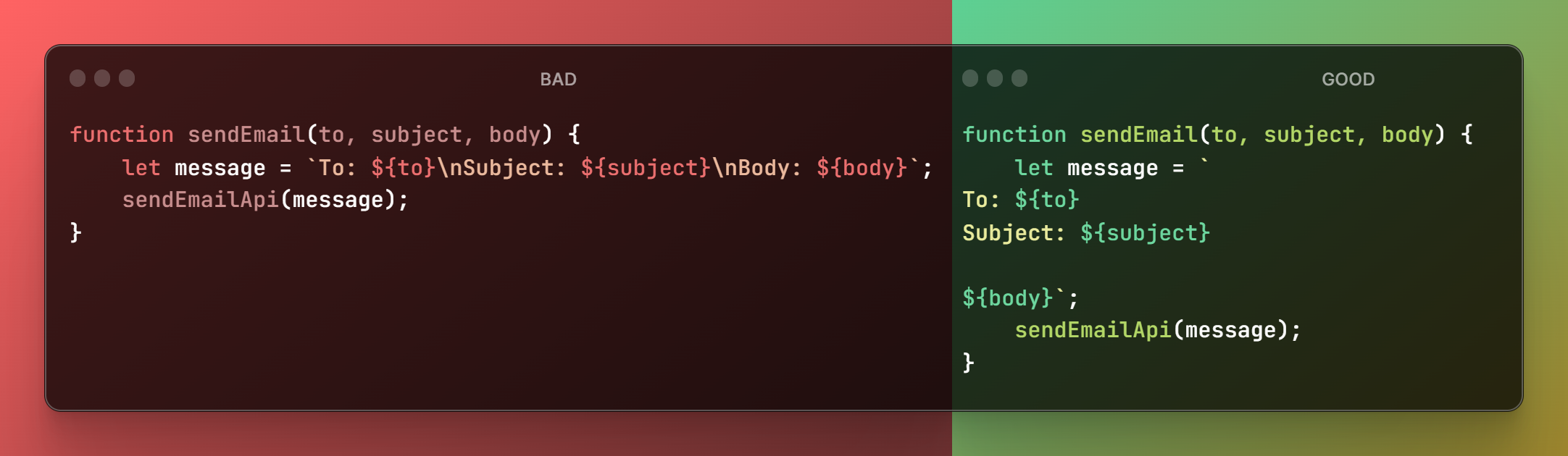
Avoid long lines of code
This usually happens when writing a long string or "if statement", it can also occur when writing functions with long names.
You can avoid most of these problems by using a code formatter. This is a friendly reminder to install a code formatter such as Prettier in your editor if you don't have it already.
Other cases to avoid long lines of code:
- Don't write long boolean expressions: "if statements" with multiple logical operations on a single line are hard to read and debug.
- Don't write nested code: it may seem clever at the moment, but it makes code harder to read and debug.
Low readability can get you fired
Software developers are expected to produce high-quality code that is reliable, maintainable, and free of errors or bugs.
It is important to write clean, well-written, and well-documented code that is easy to read and understand. This will make the code more maintainable and reduce the risk of errors, delays, and increased costs.