What is a Linear Regression and how to use it in machine learning models
Linear Regression
Linear regression is a type of model used to predict the value of a dependent variable (or target variable) based on the value of one or more independent variables (or predictor variables). Linear regression assumes that there is a direct linear relationship between the independent variables and the dependent variable. If the relationship between the target variable is one single predictor variable, the regression is said to be simple. If it has several predictors, it is called multiple regression.
This model is based on five assumptions, which are as follows:
- Linearity: The target variable and the predictor(s) have a linear relationship.
- Independence: The observations are independent of each other.
- Homoscedasticity: The variance of the errors (i.e., the differences between the model predictions and the actual data) is constant at all levels of the independent variables.
- Normality of errors: Errors are normally distributed. This is important for performing statistical tests and constructing confident intervals.
- Absence of multicollinearity: In a multiple regression, the independent variables are not perfectly correlated with each other. If there is perfect correlation, the data is said to have multicollinearity (there are variables that are the same), which makes it difficult to calculate the coefficients.
What is a Simple Linear Regression

Simple linear regression allows us to study the relationships between two continuous numerical variables. In this type of regression, we try to fit a straight line to the data that best describes the relationship between the two variables. That is, we look for a line that minimizes the vertical distance between itself and all the data points, so that the best linear relationship occurs when all the points form the line and there is no dispersion.
The equation that defines this relationship (straight line) is:
Where:
- is the dependent variable we are trying to predict or model.
- is the independent variable that we use to make the prediction.
- and are the coefficients we want the model to learn. is the intercept (value of when is zero) and is the slope.
- is the prediction error discussed above. It is the difference between the actual value of and the value of predicted by the model.
The goal of simple linear regression is, therefore, to find the best values of and that minimize the error . Once we have found these values, we can use them to predict the values of given any .
In linear regression, each dependent value has a single corresponding independent variable.
What is a Multiple Linear Regression
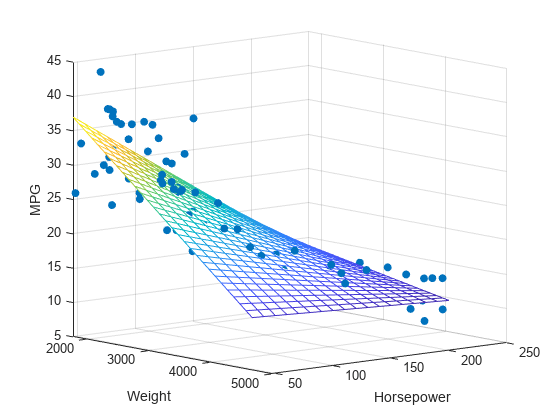
Multiple linear regression is an extension of simple linear regression used when there is more than one independent variable. It is used to model the relationship between two or more characteristics and a response by fitting a linear equation (more extended than the above) to the observed data.
The basic form of a multiple linear regression equation with n variables is:
Where:
- is the dependent variable that we are trying to predict or model.
- are the independent variables that we use to do the prediction.
- and are the coefficients we want the model to learn.
- is the prediction error discussed above. It is the difference between the actual value of and the value of predicted by the model.
Multiple linear regression allows the analyst to determine which particular variables have a significant impact on the dependent variable and by what magnitude. Like simple linear regression, this regression makes assumptions of linearity, normality, homoscedasticity, and absence of multicollinearity, and the results may be unreliable if these assumptions are violated.