Python for Data Science
Python is a highly versatile programming language used in a multitude of scenarios: web application development (both front and backend), mobile game development, simulations, networking, and automation, among others. Moreover, it is the predominant language for working with data and developing algorithms in Artificial Intelligence, Data Science, and Machine Learning. Before delving further, let's distinguish among the three aforementioned terms:
| Term | Definition | Scope | Objective |
|---|---|---|---|
| Artificial Intelligence (AI) | It is the study of making computers think and act like humans. | It's a broad field encompassing various subfields such as machine learning, robotics, natural language processing, computer vision, etc. | To simulate human intelligence in machines. |
| Machine Learning (ML) | It is a subfield of AI focused on developing algorithms and models that enable computers to learn from data. | It's a specific technique within artificial intelligence. | To make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed to do so. |
| Data Science | It is an interdisciplinary field that employs statistical, computational, and analytical techniques to interpret, understand, and extract knowledge from structured and unstructured data. | It encompasses data acquisition, cleaning, analysis, and visualization, and may make use of AI and machine learning to analyze data. | To discover patterns and glean valuable insights from large datasets. |
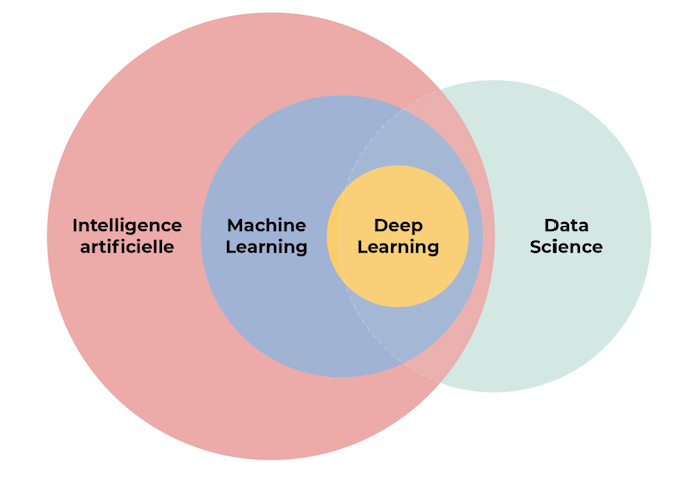
While AI focuses on simulating human intelligence, machine learning is a technique within AI that allows machines to learn from data, and data science is a broader discipline dealing with the entire process of working with data, from collection to interpretation, and may involve the use of AI and machine learning to analyze it.
Basic Python Guide
Hello, World!
Every developer starting with a new programming language typically begins by printing Hello, World!. In Python, this can be achieved using the print function, which displays any data or text placed within its parentheses:
Variables
A variable in Python (and most programming languages) is a container that stores data that can vary over time. This data can be a number, a text, a list of elements, etc. The special aspect of this container is that we can assign it a name to identify it and access what we store in it when needed:
1name = "John" 2age = 25 3height = 1.80 4is_student = True
Additionally, variables are mutable entities that can change over time. Just as we can access their value to read it, we can also modify it:
In this way, we have changed the value of the variable my_number from 10 to 60.
Variables are fundamental in programming because:
- They allow storing information for later use.
- They facilitate performing operations between them (depending on their type).
- They make the code more readable and organized. It's easier to understand
person_heightthan to remember what a lone number means in the code.
It's important to always give variables descriptive names so that we (or anyone reading our code) can easily understand what they are for and what they are supposed to contain.
Data Types
Data types determine the kind of data a variable can hold. Python has its own basic types:
Integer: int
It represents whole numbers, positive or negative.
1num_int1 = 123 2num_int2 = -57
Floating point: float
It represents real numbers with decimals.
1num_float1 = 3.14 2num_float2 = -0.16
String: str
It represents sequences of characters (text).
1str_var = "This is a sample text"
Boolean: bool
It represents values that only have two positions, True or False.
1bool_var1 = True 2bool_var2 = False
List: list
It represents an ordered collection of elements. Elements can be of any type, and their content can be modified: insert elements, delete elements, etc.
1list_numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] 2list_strings = ["A", "B", "C", "D"]
Tuple: tuple
It's similar to a list, but it's immutable; once created, its content cannot be changed.
1tuple_numbers = (1, 2, 3, 4, 5) 2tuple_booleans = (True, False, False)
Set: set
It represents an unordered collection of unique elements (no duplicates).
1set_fruits = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
Dictionary: dict
It represents an unordered collection of key-value pairs.
1dict_person = { 2 "name": "John", 3 "age": 25, 4 "height": 1.80, 5 "is_student": True 6}
Bytes: bytes
It represents sequences of bytes. Typically used for handling binary data.
1bytes_var = b"Hello"
In addition to these basic types, Python also offers modules and libraries that define other, more specialized data types.
Operators
Operators are symbols indicating an operation:
Arithmetic operators
Arithmetic operators perform arithmetic operations. Depending on the type of variables, the results may vary; they don't necessarily have to be applied only to numbers.
- Addition:
+ - Subtraction:
- - Multiplication:
* - Division:
/ - Modulus:
%
1x = 5 2y = 3 3z = x + y # Output: z = 8 4z = x * y # Output: z = 15
Logical operators
Logical operators evaluate conditions and return boolean values. They can be used in loops, conditionals, filters, etc. They are very versatile and useful.
- Logical AND: and
- Logical OR: or
- Logical NOT (negation): not
1result = True and False # result = False 2result = True or False # result = True 3result = not True # result = False
Control Structures
Control structures in Python are instructions that modify the execution flow of a program. These structures allow making decisions, repeating code blocks, and jumping to different parts of the code depending on certain logical conditions.
In Python, the main control structures are:
Decision structures
if
Allows executing a code block if a condition is met.
elif
Extends the if to include and check other conditions.
else
It executes when none of the previous condition(s) are met:
Loop Structures
for
Repeats a code block a certain number of times or through the elements of a collection.
while
Repeats a code block while a condition is met.
Loop Control
break
Terminates the loop before it completes all its iterations.
continue
Jumps to the next iteration of the loop, skipping the code that follows.
pass
Does nothing. It acts as a placeholder where a syntactically required statement is needed, but no code needs to be executed.
These control structures are essential for creating programs that can make decisions, repeat tasks, and handle different situations or inputs. By combining and nesting them, we can create complex workflows and sophisticated logic in our programs.
Functions
A function is a reusable block of code that performs a specific task.
Functions provide a way to modularize code, allowing us to organize and reuse code snippets in different parts of our programs. This improves quality and makes debugging and maintenance easier.
A Python code combines all the elements we've just seen in this guide to carry out a specific task. Below is a simple program that takes the age of a user, determines whether they are a minor, adult, or senior, and then prints a list of recommended activities for each group:
Libraries
A library is a collection of predefined functions designed for a specific purpose. The goal is to simplify the developer's work and avoid programming them from scratch. There are many libraries, organized according to their usefulness. As Python is the most used language in the fields of Data Science and Artificial Intelligence, some of its most used libraries are related to these fields:
- Scikit-learn
- NuPIC
- Ramp
- NumPy
- Pandas
- TensorFlow
- Keras
- Pipenv
- SciPy
- Matplotlib
Out of this top 10, most are used in processes like Machine Learning, Natural Language Processing, Computer Vision, and many other areas of Artificial Intelligence. Therefore, it's vital to know and be able to use some of these libraries, as they are key to any data science task.
In this bootcamp, we'll delve deeply into NumPy, a library used to process and work efficiently with multidimensional arrays, Pandas, built on top of NumPy, allowing work with tabular data structures called DataFrames. Matplotlib, enabling data visualization, and scikit-learn, widely used for building Machine Learning models.
Performance
All software that is programmed must run on hardware, which is a set of physical elements constituting a computer system. The more efficient the code you implement, the better the hardware resource utilization, lower execution times, greater possibility of distributing tasks, and so on.
When building artificial intelligence models, performance is a major concern, as processing power is the biggest limitation in this field at the moment. Therefore, building efficient code and functions is a fundamental pillar. We will also learn about this.
Code Development
There are two main ways to program in Python, and each of them can be carried out using different tools:
- Flexible programming: It is carried out with web interfaces like
Jupyter NotebookorGoogle Colab. It is characterized by not having a predefined code structure and is designed for rapid development and trial and error. In this type of development, notebooks are generated. - Productive programming: It is carried out in Integrated Development Environments (IDEs), which are software programs that allow end-to-end development of an application or a complete service. Some of the most used in Python are
Visual Studio CodeandSpyder, among others.
Normally, the development of a product, model, or service for Machine Learning consists of two phases: an exploratory phase and a development phase. First, we program in notebooks and conduct proof of concept tests, seeking the best data preprocessing, analysis, and prediction, and then we prepare a complete development to operationalize the model.
Project Structure
We will use a template for our projects called Cookie Cutter Datascience. Using a template is always a good idea to organize our files and project workflow. You can read the documentation and watch this video on how it works.