Introduction to Numpy

Introduction to NumPy¶
NumPy means Numerical Python. It is an open-source library used to perform mathematical tasks with very high efficiency. In addition, it introduces data structures, such as multidimensional arrays, which can be operated on at a high level, without getting too much into the details.
Specifically, the keys to this library are:
- Multidimensional arrays: This library provides an object called
ndarray, which allows you to store and manipulate large data sets efficiently. Arrays can have any number of dimensions. - Vectorized operations: NumPy allows performing mathematical operations on complete arrays without the need for explicit loops in the code, which makes it very fast and efficient.
- Mathematical functions: NumPy provides a wide range of mathematical functions for working with arrays, including trigonometric functions, statistics, and linear algebra, among others.
- Efficiency: It is much faster than the same functionality implemented directly on native Python. It is also very flexible in terms of accessing and manipulating individual elements or subsets of arrays.
NumPy is a fundamental library for Machine Learning and data science in Python. It provides a wide range of tools and functions to work efficiently with numerical data in the form of arrays and matrices.
Arrays¶
A NumPy array is a data structure that allows you to store a collection of elements, usually numbers, in one or more dimensions.
One-dimensional Array¶
A one-dimensional (1D) array in NumPy is a data structure that contains a sequence of elements in a single dimension. It is similar to a list in Python, but with the performance and functionality advantages offered by NumPy.
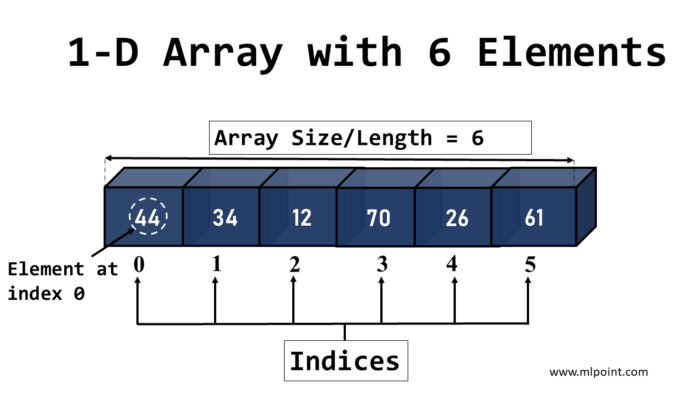
A 1D array can be created using the array function of the library with a list of elements as an argument. For example:
import numpy as np
array = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
array
This will create a 1D array with elements 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5. The array elements must be of the same data type. If the elements are of different types, NumPy will try to convert them to the same type if possible.
In a 1D array, we can access the elements using indexes, modify them and perform mathematical operations on the whole array efficiently. Below are some operations that can be performed using the above array:
# Access the third element
print(array[2])
# Change the value of the second element
array[1] = 7
print(array)
# Add 10 to all elements
array += 10
print(array)
# Calculate the sum of the elements
sum_all = np.sum(array)
print(sum_all)
N-dimensional Array¶
A multidimensional or n-dimensional array in NumPy is a data structure that organizes elements in multiple dimensions (axes). These arrays allow you to represent more complex data structures, such as matrixes (2D array, 2 axes), tensors (3D array, 3 axes) and higher-dimensional structures.
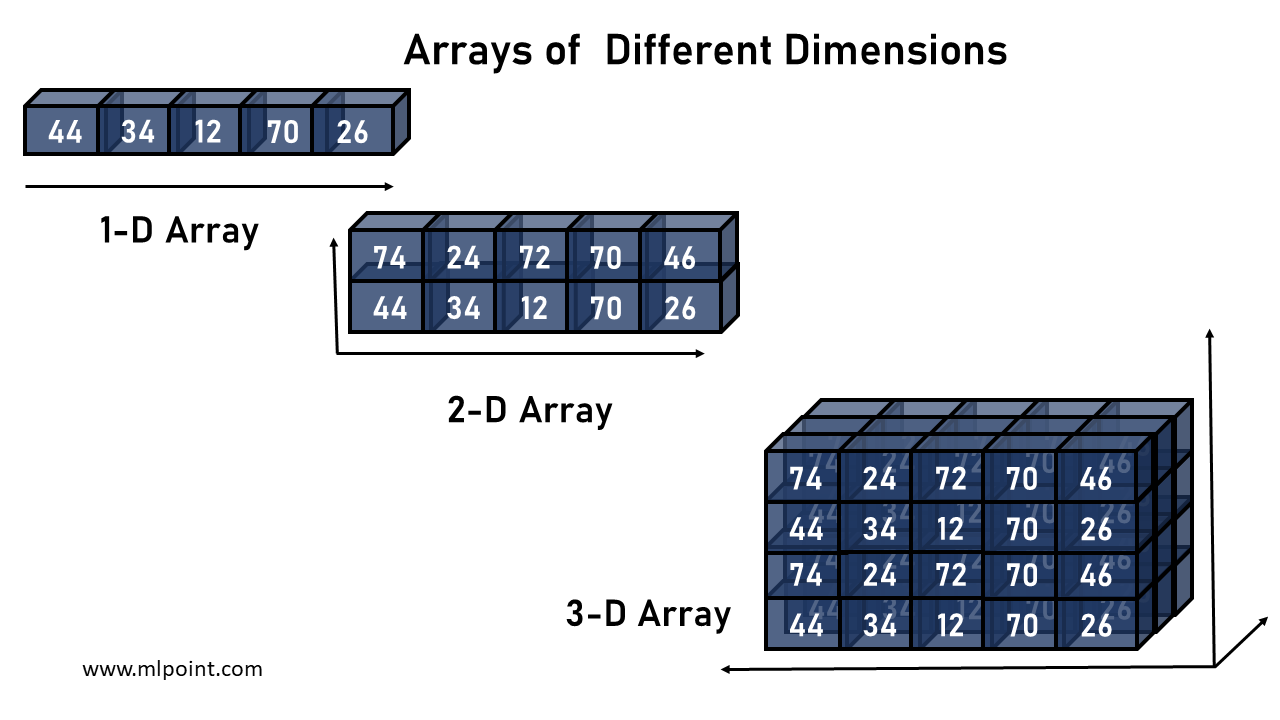
An N-dimensional array can also be created using the array function of the library. For example, if we want to create a 2D array:
array_2d = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]])
array_2d
If we now wanted to create a 3D array, we would have to think of it as a list of arrays:
array_3d = np.array([[[1, 2], [3, 4]], [[5, 6], [7, 8]]])
array_3d
As with 1D arrays, the elements in a multidimensional array are accessible via indexes, operations can be performed on them, and so on.
As we add more dimensions, the basic principle remains the same: each additional dimension can be considered an additional level of nesting. However, on a practical level, working with arrays of more than 3 or 4 dimensions can become more complex and less intuitive.
The n-dimensional arrays in NumPy allow great flexibility and power to represent and manipulate data in more complex ways, especially useful in fields such as data science, image processing and deep learning.
Functions¶
NumPy provides a large number of predefined functions that can be applied directly to the data structures seen above or to Python's own data structures (lists, arrays, etc.). Some of the most commonly used in data analysis are:
import numpy as np
# Create an array for the example
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
# Arithmetic Operations
print("Sum:", np.add(arr, 5))
print("Product:", np.multiply(arr, 3))
# Logarithmic and Exponential
print("Natural logarithm:", np.log(arr))
print("Exponential:", np.exp(arr))
# Statistical Functions
print("Mean:", np.mean(arr))
print("Median:", np.median(arr))
print("Standard Deviation:", np.std(arr))
print("Variance:", np.var(arr))
print("Maximum value:", np.max(arr))
print("Maximum value index:", np.argmax(arr))
print("Minimum value:", np.min(arr))
print("Minimum value index:", np.argmin(arr))
print("Sum of all elements:", np.sum(arr))
# Rounding Functions
arr_decimal = np.array([1.23, 2.47, 3.56, 4.89])
print("Rounding:", np.around(arr_decimal))
print("Minor integer (floor):", np.floor(arr_decimal))
print("Major integer (ceil):", np.ceil(arr_decimal))
Exercise 01: Create a null vector that contains 10 elements (★☆☆)¶
A null vector is a one-dimensional array composed of zeros (0).
NOTE: Check the function
np.zeros(https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/generated/numpy.zeros.html)
Exercise 02: Create a vector of ones with 10 elements (★☆☆)¶
NOTE: Check the function
np.ones(https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/generated/numpy.ones.html)
Exercise 03: Investigate the linspace function of NumPy and create an array with 10 elements (★☆☆)¶
NOTE: Check the function
np.linspace(https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/generated/numpy.linspace.html)
Exercise 04: Find several ways to generate an array with random numbers and create a 1D array and two 2D arrays (★★☆)¶
NOTE: Check the functions
np.random.rand(https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/random/generated/numpy.random.rand.html),np.random.randint(https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/random/generated/numpy.random.randint.html) andnp.random.randn(https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/random/generated/numpy.random.randn.html)
Exercise 05: Create a 5x5 identity matrix (2D array) (★☆☆)¶
NOTE: Check the function
np.eye(https://numpy.org/devdocs/reference/generated/numpy.eye.html)
Exercise 06: Create a 3x2 random number matrix and calculate the minimum and maximum value (★☆☆)¶
NOTE: Check the functions
np.min(https://numpy.org/devdocs/reference/generated/numpy.min.html) andnp.max(https://numpy.org/devdocs/reference/generated/numpy.max.html)
Exercise 07: Create a vector of 30 elements that are random numbers and calculate the mean. (★☆☆)¶
NOTE: Check the function
np.mean(https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/generated/numpy.mean.html)
Exercise 08: Converts the list [1, 2, 3] and the tuple (1, 2, 3) to arrays (★☆☆)¶
Operations between arrays¶
Exercise 09: Invert the vector of the previous exercise (★☆☆)¶
NOTE: Check the function
np.flip(https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/generated/numpy.flip.html)
Exercise 10: Change the size of a random array of dimensions 5x12 into 12x5 (★☆☆)¶
NOTE: Check the function
np.reshape(https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/generated/numpy.reshape.html)
Exercise 11: Convert the list [1, 2, 0, 0, 0, 4, 0] into an array and get the index of the non-zero elements (★★☆)¶
NOTE: Check the function
np.where(https://numpy.org/devdocs/reference/generated/numpy.where.html)
Exercise 12: Convert the list [0, 5, -1, 3, 15] into an array, multiply its values by -2 and obtain the even elements (★★☆)¶
Exercise 13: Create a random vector of 10 elements and order it from smallest to largest (★★☆)¶
NOTE: Check the function
np.sort(https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/generated/numpy.sort.html)
Exercise 14: Generate two random vectors of 8 elements and apply the operations of addition, subtraction and multiplication between them (★★☆)¶
NOTE: Check the math module functions: https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/routines.math.html
Exercise 15: Convert the list [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12] into an array and transform it into a matrix with rows of 3 columns (★★★)¶