Event Driven Programming
Javascript
HTML and CSS
Event Driven Programming
Event Driven Programming
Working with events is a totally new way of controlling the flow of an application. It is the first time that your code will not be executed in a linear flow, which is how JavaScript is generally programmed to execute, from the first line of code to the last.
Instead, your code will now be executed asynchronously (i.e. some pieces of code will not work when the rest of the surrounding code is being executed, but only when they are explicitly triggered). Who knows what comes first?
What is an Event?
An event is something that happens during the runtime of your web application! Such as clicking on a button, pressing a key on the keyboard, hovering a <div> with your mouse, etc.
Your job as a developer is to prepare for those events and define handler functions - the actions that are going to be handling each event.

But who Triggers these Events?
Sometimes it is the website user, sometimes it is the browser, sometimes it is another application letting you know something, sometimes the developer triggers events related to the business logic, etc.
There are dozens of events being triggered every minute, but you don’t have to do anything about them (not if you don’t want to). They are available to you depending on the type of application that you want to make.
Types of Events
Here are some of the types of events that are constantly being triggered (and you can listen to them):
MOUSE – Events
| Data-Type | Description |
|---|---|
| click | When the user clicks with the mouse on any HTML element. |
| mouseover, mouseout | The event occurs when the pointer is moved onto (for mouseover) or outside (for mouseout) an element or one of its children. |
| contextmenu | When the user right-clicks on the mouse. |
| mousemove | If the user moves the mouse. |
| mousedown, mouseup | If the user presses or releases the mouse. |
☝ Play with this demo here
FRAME – Events
| Data-Type | Description |
|---|---|
| load | The browser has finished loading the website. |
| error | The event occurs when an error occurs while loading an external file (like CSS or JavaScript). |
| scroll | When the element or window gets scrolled. |
| pagehide, pageshow | When the user focuses on a different window / tab, or when the user comes back from a different window / tab. |
| resize | When the window is resized. |
☝ Play with this demo here
FORMS – Events
| Data-Type | Description |
|---|---|
| submit | The event occurs when a form is submitted. |
| focusin, focusout | The event occurs when the pointer is moved onto an element or onto one of the element’s children. |
| input | The event occurs when an element receives user input. |
| change | The event occurs when the content of a form element, the selection, or the checked state has changed (for <input>, <keygen>, <select>, and <textarea>) |
☝ Play with this demo here
KEYBOARD – Events
| Data-Type | Description |
|---|---|
| keyup | When the user releases a keyboard key. |
| keydown | When the user presses a keyboard key. |
| keypress | When the user presses and releases a keyboard key. The difference from keydown/up is that keypress only works on character keys. For example, it does not work on the up|down|left|right arrows. |
☝ Play with this demo here
Listening for events
Now that you know the main events that exist out there, you can start listening to them during the runtime. The only way to react to any event is by listening for that event and assigning a function that will handle the event however you need.
Let’s repeat: To react you need to listen. And to listen, you need to specify a handler function. We call that construct an Event Listener.
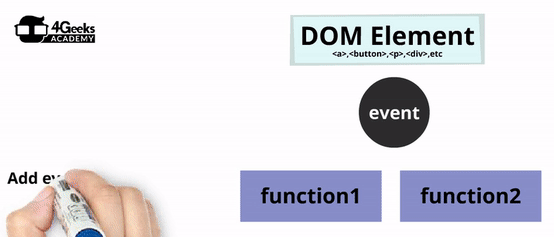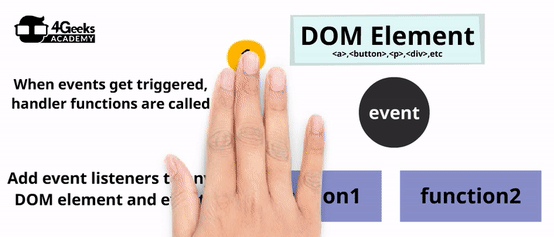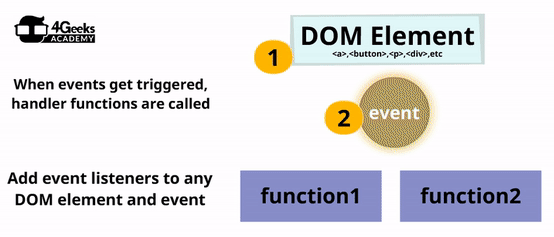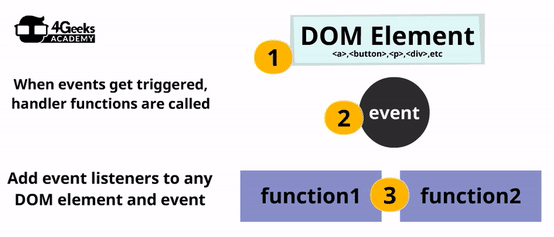
You can add an event listener in 2 different ways:
Adding Listeners from the HTML
For example, if you want to start listening when the user clicks on a particular button, all you have to do is specify the "onclick" attribute to that specific HTML <button> tag, like this:
1<!-- myClickHandler is a JavaScript function that will handle the event --> 2<button onclick="myClickHandler()">Click me</button> 3 4<script> 5function myClickHandler() { 6 alert('hello'); 7} 8</script>
Adding Listeners from JavaScript (during runtime)
Sometimes the DOM elements don't exist from the beginning. Maybe they are created after a database call or after the user did something. To solve that problem, you need to start listening after the new elements are created.
The .addEventListener() function is perfect for this because it can be used in any DOM element during runtime.
When using the .addEventListener() function, you have to specify what event you want to listen to, and the handler function that will be called every time that event is triggered on that DOM element.
For example, the code below is creating a list of names, and each <li> in it is listening for the "click" event, which then triggers the removal of the same <li>:
The Event Object
Event handler functions can receive one optional parameter in their declaration, which most developers name event, evt, or simply e. This parameter is always filled with the "Event object" which gets sent by default from every event and contains important information about the event that was triggered, the element where it occurred, its value, etc.
1function myEventHandler(eventObj) { 2 console.log(eventObj.target); 3 // will print on the console the DOM element that triggered the event 4 console.log(eventObj.type); 5 // will print on the console the type of event 6 console.log(eventObj.cancelable); 7 // will print on the console true or false if the event can be canceled 8 eventObj.preventDefault(); 9 // will prevent the default action of the event if allowed 10 eventObj.stopPropagation(); 11 // will prevent the propagation of the event if allowed 12}
Every Event Object has the following Properties:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| target | Returns the DOM element that triggered the event. |
| type | The type of event: click, mouseover, load, etc. |
| cancelable | If you can stop the event's default action or not. |
| preventDefault() | If the event is cancelable, this method stops the default action of it; for example, preventing a "submit" event of a form will result in the form not being submitted, which can be useful if the form has errors that need to be corrected, etc. |
| stopPropagation() | Stops an event from propagating (i.e. from triggering the same event in nested or parent elements). |
Depending on the type of event, you will have additional properties that will give you very useful information about what happened when the event was triggered.
One of the most important such additional properties is the target.value property of the event objects related to input fields. It allows us to capture and save the user input from input elements.
You can do it by passing the 'event' argument in the inline onchange event's handler function:
1<input type="text" onchange="myChangeHandler(event)" /> 2 3<script> 4const myChangeHandler = (e) => { 5 console.log(e.target.value); 6 // Will print on the console whatever the user types into the input field 7} 8</script>
Or, you can do it with addEventListener:
index.html:
1 <input type="text" />
index.js:
1 const myChangeHandler = (e) => { 2 console.log(e.target.value); 3 } 4 5 document.querySelector("input").addEventListener('change', myChangeHandler);
Notice that in addEventListener() we only reference the function (myChangeHandler) and do not actually call it (myChangeHandler()). If you call it, it will automatically run when the page loads and not wait for an event to be triggered, which is highly undesirable. Therefore, we do not need to pass the Event object as an argument there (there are no parentheses). The event object is passed automatically by the addEventListener() to the handler function.
Additional information for mouse events
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| clientX, clientY | Returns the horizontal or vertical coordinate of the mouse pointer, relative to the current window, when the mouse event was triggered. |
| pageX, pageY | Returns the horizontal or vertical coordinate of the mouse pointer, relative to the document, when the mouse event was triggered. |
| which | Returns which mouse button was pressed when the mouse event was triggered. |
Additional information for keyboard events
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| keyCode | Returns the Unicode character code of the key that triggered the event. |
| shiftKey, altKey or ctrlKey | Returns whether the shift, alt or ctrl key was pressed when the key event was triggered. |
Additional information for wheel events
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| deltaX, deltaY | Returns the vertical or horizontal scroll amount of a mouse wheel (y-axis) or (x-axis). |
| deltaMode | Returns a number that represents the unit of measurement for delta values (pixels, lines, or pages). |
🔗 There is a lot more information you can get from the event object, but we are focusing on the most used properties. For a bigger list of properties, please read this guide.
Removing the Listeners
But what if I don’t want to continue listening? All modern browsers remove the events listeners when you delete the DOM element in which they were applied. If you don’t want to delete the DOM element, you can remove the listener manually using the .removeEventListener() function.
1element.removeEventListener(type, eventHandlerFunction);
You have to use the exact same parameters in the removeEventListener() function as the ones you used in the addEventListener() function.
Here is an example:
In this code, we are adding an event listener to the click event. Afterward, the first time the click listener gets called, the handler function removes the event listener from the button. That’s why the second time the button gets clicked, nothing happens.