Data backup and recovery
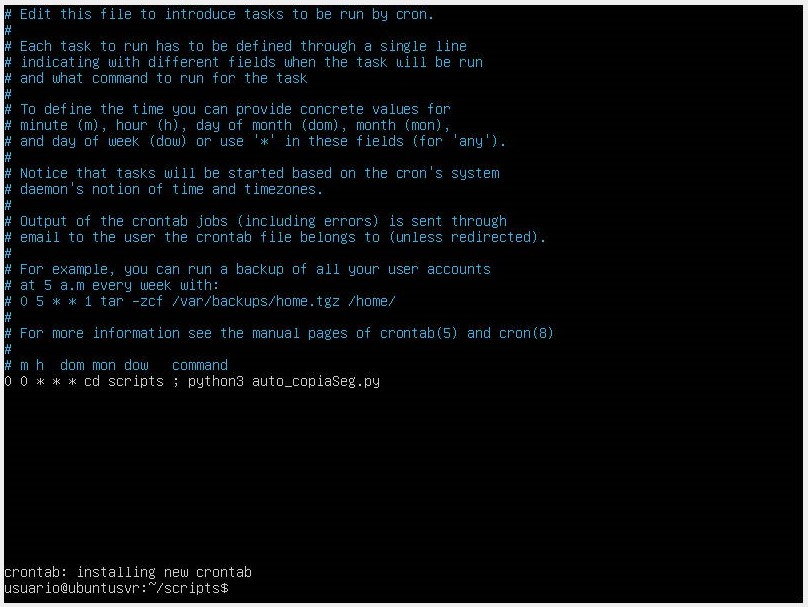
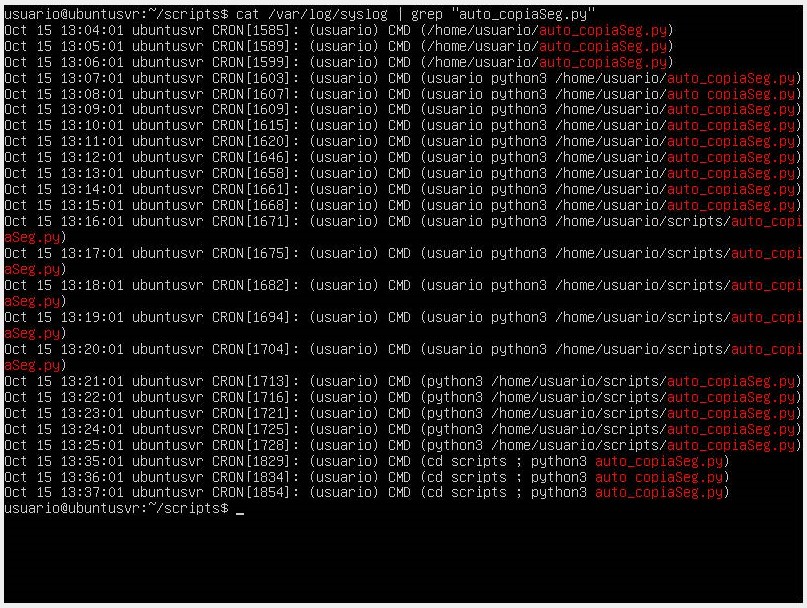
Backup Planning and Retention Policies
As cybersecurity analysts and security administrators, backup planning and retention policies are critical aspects of our work, as they ensure the protection and availability of stored data. These practices are fundamental to ensuring the integrity of information and the ability to recover from possible incidents or data loss.
Some important aspects to consider when working on backups are:
| Identifying Critical Data | The first step is to identify the most important data on the Linux server. This can include configuration files, databases, log files, and any other essential data for the infrastructure's operation. These data should be backed up frequently and as a priority. |
|---|---|
| Selecting the Backup Tool | There are several backup tools available for Linux servers, such as rsync, tar, Bacula, and others. It is important to select a tool that fits the specific needs of your server and allows efficient and reliable backups. |
| Defining the Backup Strategy | The backup strategy can include full, incremental, or differential backups. Full backups copy all selected data, while incremental and differential backups only back up changes made since the last backup. It is important to evaluate which strategy best suits your needs in terms of time, storage space, and recovery capability. |
| Scheduling Backups | It is advisable to establish a regular schedule for backups. This can include daily, weekly, or monthly backups, depending on the criticality of the data and the frequency of changes on the server. Additionally, it is important to consider the impact on server performance during the backup process. |
| Secure Storage | Backups should be stored in a secure location off the Linux server. This can include external storage devices, remote backup servers, or cloud services. It is essential to ensure that backups are protected against unauthorized access and physical disasters. |
Regarding retention policies, it is important to establish how long backups should be stored before being deleted. Some aspects to consider are:
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Ensure compliance with applicable laws and regulations regarding data retention. This can vary depending on the industry and geographical location.
- Operational Requirements: Consider your organization's operational requirements, such as internal or external audits, contractual agreements, or disaster recovery needs. These requirements can influence the retention duration of backups.
- Periodic Review and Update: It is recommended to regularly review and update retention policies to ensure they remain adequate and aligned with changes in the organization and the legal environment.
Using Backup and Recovery Tools
Ensuring the protection and availability of stored data is an essential and important task within our functions as server administrators. To achieve this, we can rely on backup and recovery tools that allow us to make data backups and facilitate recovery in case of loss, damage, or corruption.
Some popular tools are:
| rsync | A synchronization and backup tool that allows copying and synchronizing files and directories between local or remote systems. Rsync uses efficient algorithms to transfer only the differences between files, reducing the time and bandwidth required for backups. |
|---|---|
| tar | An archiving tool that allows creating compressed files from directories and individual files. Tar is commonly used in combination with other tools, such as gzip or bzip2, to compress backup files and save storage space. |
| Bacula | An open-source backup and recovery solution that offers a wide range of features and functionalities. Bacula allows performing full, incremental, and differential backups and offers advanced options such as backup scheduling, retention policy management, and granular file recovery. |
| Amanda | Another open-source backup and recovery tool widely used on Linux servers. Amanda allows efficient and scalable network backups and offers features such as data deduplication, compression, and encryption. |
| Duplicity | A backup tool based on the rsync protocol that offers incremental and encrypted backups. Duplicity integrates well with cloud services such as Amazon S3 or Google Drive, allowing secure and off-server Linux backups. |
When using these backup and recovery tools, it is important to follow best practices, such as:
- Regularly and scheduled backups, ensuring the inclusion of critical and relevant data for the organization.
- Storing backups in a secure location off the Linux server, preferably on external storage devices or cloud services.
- Verifying the integrity of backups to ensure they can be correctly recovered if necessary.
- Documenting and testing recovery procedures to ensure efficient and successful data recovery in case of loss or disaster.
Backup Verification Tests
Backup verification tests are a fundamental part of the backup and recovery strategy. These tests ensure that backups have been performed correctly and that data can be successfully recovered if needed.
Here are some key points to consider when performing backup verification tests on Linux servers:
-
Verification of Backup Integrity: It is important to ensure that backups are complete and have not been damaged or corrupted during the backup process. Tools like md5sum or sha256sum can be used to calculate the hash of the backed-up files and compare them with the original hashes. If the hashes match, it indicates that the backups are intact.
-
Restoration of Test Data: An effective way to verify backups is to perform test data restorations in a test environment. This involves selecting some backup files or directories and restoring them on a separate server or virtual machine. By performing this test, you can confirm that the backed-up data can be correctly recovered and is in a usable state.
-
Verification of Data Consistency: In addition to verifying the integrity of backups, it is important to ensure that the backed-up data is consistent and in a usable state. This involves verifying that the backed-up files and directories are accessible and that there are no errors or inconsistencies in their content.
-
Disaster Recovery Tests: Disaster recovery tests are essential to evaluate the recovery capability of backups in critical situations. These tests involve simulating a total server loss scenario and performing data recovery using backups. By performing these tests, you can evaluate the effectiveness of backups and recovery procedures.
-
Documentation and Tracking: It is important to document and track backup verification tests. This includes recording test results, identifying any problems or inconsistencies found, and taking necessary measures to correct them. Additionally, it is recommended to establish a regular schedule for performing backup verification tests and ensure they are conducted periodically.