penetration testing
cybersecurity
What is Nmap and how to use it
We can only talk about pen-testing and vulnerability scanning by analyzing one of the most powerful, complete, and veteran scanners we can find on the net: Nmap.
This software is one of the most used to search for hosts within a local network, but it also allows the discovery of hosts on the Internet to check if they are connected to the network, in addition, we can perform extensive and advanced port scans to check if we have any service running that is not protected by the firewall, and we can even see if we have a firewall on a particular host. Another option that we can perform with this program is to know what operating system a specific host uses, if we scan a computer with Windows it will indicate that we are indeed scanning a Windows operating system, and the same with Linux or Unix.
This program is open source and multiplatform, although the most common is using it on Linux operating systems to perform the task of pen-testing. It is the first step to perform an intrusion into the systems and try to hack the computer properly, always with ethical purposes to discover possible vulnerabilities.

This software has a lot of advanced options and also has an optional graphical interface called Zenmap that we can use quickly and easily.
It is an essential tool, as it allows us to identify potential vulnerabilities that could be used as entry points by attackers. By running NMAP on a specific target we could observe those devices, servers, services, firewalls, and more, related to the first one. To do this, the tool sends different types of packets (ping, echo, and port directed) to probe an IP or a range of IPs.
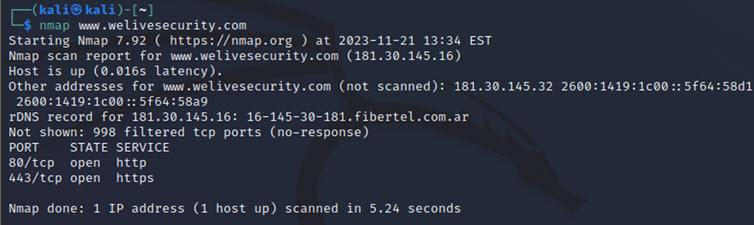
Using NMAP through the command line
Usually, this tool is executed via terminal (although there are adaptations with a graphical interface) with the format:
1$ nmap <Flags> <Target>
The execution without parameters runs a simple scan to the 1000 most common ports, previously performing a ping to see if the computer is alive (if the computer does not respond to the ping, the port test will not be performed).
NMAP Command Line Flags
Countless Flags will indicate particular configurations to the execution. Among the most commonly used, we find:
-
-sn, to determine if a target is available.
-
sT, to determine which ports are open on a target using TCP.
-
O, to identify the operating system and software version running on a target.
-
A, for the complete scan of the target.
Identifying a vulnerability in a port provides the attacker with an excellent attack vector that, with luck and expertise, can cause the machine to be compromised. It is a very flexible tool with a multitude of options.
Nmap with NSE Scripts
Although this tool was born as a port scanner, thanks to the NSE scripts included by default (which can be downloaded from a multitude of web pages) it is possible to use it as a complete tool to search for vulnerabilities in networks and systems. The NSE scripts use the power of Nmap itself, but it is also capable of exploiting known vulnerabilities in certain programs, so it is very useful to update it frequently with the latest scripts. Both NSE and Nmap make a really powerful team to help the hacker to perform pentesting.
Some of the functions we can perform are attacking Samba servers by testing hundreds of users and passwords, the same with FTP servers and even SSH servers, and we can attack a large number of services to exploit vulnerabilities.
🔥 When a public vulnerability is released, developers incorporate this exploit in Nmap NSE to exploit it easily and quickly, in order to help pen-testers in the task of exploiting the compromised system.
Reasons to use Nmap
- It can quickly recognize all devices, including servers, routers, and cell phones, among others. And it can do so in both single and multiple networks. So it is a very good choice for the business sector where different networks are used.
- It helps us to make an identification of the services running on the system. Web servers, DNS, and other applications will be scanned as well. This makes it possible to detect different versions of the applications very accurately. This helps to detect existing vulnerabilities.
- You can locate information about the operating systems running on the devices. It also provides very detailed information such as the versions of the packages, which helps us a lot in planning different approaches during the penetration of the packages.
- In security audits and vulnerability scanning, Nmap can attack systems by using existing scripts in the Nmap scripting engine.
- It has a graphical interface called Zenmap, which helps us to perform visual mappings of networks. This is good for giving greater usability to the tool and makes it easier for reports to be generated in a more detailed, intuitive, and accessible way.
Advantages of NMAP
With Nmap, we can obtain a series of advantages, which not only will help us to have more functionalities but also can influence us in its ease of use. Some of them can be:
- The operating system determines when Nmap can scan open ports. At least one of them has to be open on the system when scanning.
- Open ports that are listening can be determined, but often this port may not identify the operating system.
- If an attempt is made to identify the OS generation by probing, an overlay may be created based on the information determined from the probe itself, and this will not be considered authoritative. After all, the OS identification is determined by an algorithm that performs an analysis of the open ports. Many elements can make this identification erroneous.
Disadvantages of NMAP
But as in everything, we will find some disadvantages, which can make us change our mind about whether to use it or not. For example:
- Nmap can be used as a hacker tool. In any case, it is possible that the security of the equipment does not allow it.
- NCAP is required and a filter driver for the network must be installed. NCAP can interact with other software, and in turn, cause problems through operational overruns.
- NCAP and NMAP are intended to be transparent, however, they may have interactions with software installed in the environment. This can be a concern for any administrator, so it is recommended to perform the appropriate tests to use it.
- Scanned devices may respond unexpectedly, especially if they are very different from the usual machines, such as medical equipment, for example.
- It can be blocked by local firewalls, both on the system performing the scan and on the system being scanned. This can limit the available data considerably.
- It may be blocked by software such as antivirus software, for example. This can affect the depth and accuracy of all data provided by Nmap.
- Nmap's methodology tries to be as efficient as possible, but it may not be able to perform scans at certain points on the local network where it is performing scans.
NMAP Alternatives
NMAP is not the only tool we can find. Many on the internet can do the function properly, even some with new features. For example:
- FING: It is an option oriented to mobile devices. It allows us to perform a quick analysis of the network where we are connected. With facilities to detect intruders and perform control over the activity carried out on the network.
- Angry IP Scanner: Once again this is a multiplatform program. Free and with the possibility of performing an analysis of several network interfaces. It is very fast when scanning ports.
- WinMTR: In this case we are dealing with an example that is very easy to use and also free. But it is only available for Windows, which limits it a bit. It can diagnose problems in the connections, and at the same time, it gives us ping and traceroute options. Anyway, it is one of the most basic.
- Scapy: Here we do not find a network analyzer. But it does allow us to manipulate packets, and act as a sniffer. This makes it possible to decrypt WEB packets, analyze VLANs, and check VoIP networks. It is one of the most complex of the whole list.
- Fingbox: It is a good option for both mobile and desktop computers. It has a free version, but the most complete version is paid.