Data Structures
Arrays
Javascript
What is an Array? Understanding the Basics and Defining Array Data Structure
An array is a data structure that stores a fixed-size collection of elements such as integers or strings, sequentially in memory. Each element in the array is accessed using an index, starting from zero. Arrays provide fast access to elements and are commonly used for efficient data storage and manipulation. They offer benefits in terms of memory allocation and cache efficiency, making them valuable in various programming tasks, from simple data storage to complex algorithms and computations. However, their fixed size can be a limitation, requiring careful management to avoid overflow or underflow issues.
Why are Arrays in a Separate Lesson?
Because arrays are awesome! You need them! And we need to focus a lot on them in order to prepare you for real life. 🙂
Mastering the use of arrays and loops is one of the 5 fundamental skills of building algorithms:
Variables.Conditionals.Arrays.Loops.Functions.
No, no, no... Wait... Arrays? What?
An array is, normally, any list or collection of values. The rules of how to add or remove elements from that list can change from one programming language to another. But (generally) they are the only ways for developers to create elements.
Arrays are the only way we have to list stuff; regardless of the application you are working with, it will always have things to list. For example, list of students, list of artists, list of transactions... anything!
This data-type does a lot more stuff than the others. Lists are one of the only ways to store more than one data-type in the same variable.
Every array has the same basic concepts:
The items: are the actual values inside each position of the array.
The length: is the size of the array (how many items the array has).
Index: is the position of the element.
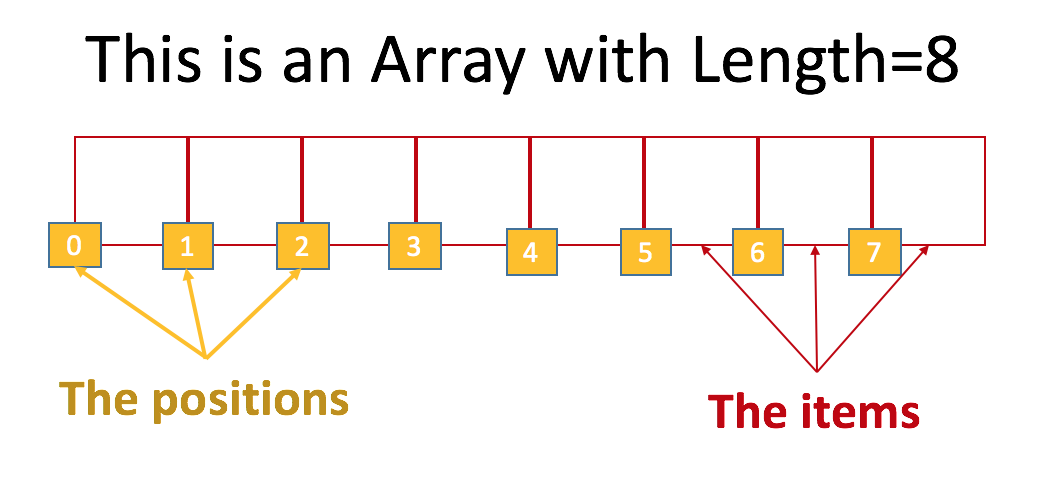
☝ Array positions start at zero (0); the first element is the element in the position zero (0).
How to Declare an Array?
These are different examples of list declarations:
1let myArray = []; // Empty list 2let myArray = ["Apple", "Orange", "Donkey"]; // With 3 string items 3let myArray = new Array(1,2,3,4,5); // Don't use this! Read below to learn why
☝ Don't declare the Arrays with the
new Array()syntax, it will not behave properly. Click here to learn the details.
Access Items in the Array
To access a specific element in a list, you need an index. We call index the integer value that represents the position of the element you want to access/get/retrieve.
The index must always start at zero (0). That means that an Array of 2 items can have index = 0 or index = 1. Trying to get the 2nd position will return undefined because it will mean that we are trying to access the third element (which does not exist). For example, to get any items in the array you can do the following:
1 console.log(myArray[0]); // This will print the 1st element in the console 2let aux = myArray[5]; 3 console.log(aux); // This will print the 6th element in the console 4 console.log(myArray[myArray.length-1]); // This will print the last element of the array
Update Items in the Array
If you want, you can reset or update any item inside an array using the index like this:
1myArray[5] = 'Whatever value'; 2// This will set the value 'Whatever value' to the 6th element in the array
Adding Elements (push function)
To add a new element at the end of your array you will need to use the push() function.
But... what if I want to add Chris in the second position?
Then... you need to create a new empty array and start pushing the elements in the order that you need them. In this case, it will be:
Removing Elements (pop function)
Removing an element has the exact same limitations as adding an element: you can only remove an element from the last position using the pop() method. If you want to remove a different element, you will need to create a new array without that particular element.
Removing/Adding from the Beginning
The shift() and unshift() methods are just like push() and pop(), but with the difference that they will only work from the very beginning of the list.
Looping an Array
Sometimes, when working with arrays, you will need to loop them. For example, sorting them manually; flipping them; deleting an element from a particular position, etc.
In order to create your loop, you will need to use Array.length to get the current size of the array. Most of the time the array items change during the runtime. This is why the only way to get the size of the array will be by using the Array.length function, like this:
For…in…
There is a great adaptation of the for statement to make it loop lists or arrays, like this:
1let myArray = [3423,5,4,47889,654,8,867543,23,48,56432,55,23,25,12]; 2 for (let index in myArray) { 3 console.log(myArray[index]); 4} 5// This prints the value of the item in the position [index]
Removing from an Array
It is possible to cut an array into pieces very fast, with the slice() and splice() functions.
Slice
Will return a new array, you have to specify the starting and ending index from where you want to cut the array.
Splice
Will update the current array, returning the items you want to retrieve. You will need to specify the starting index and how many items you want to retrieve from said index.
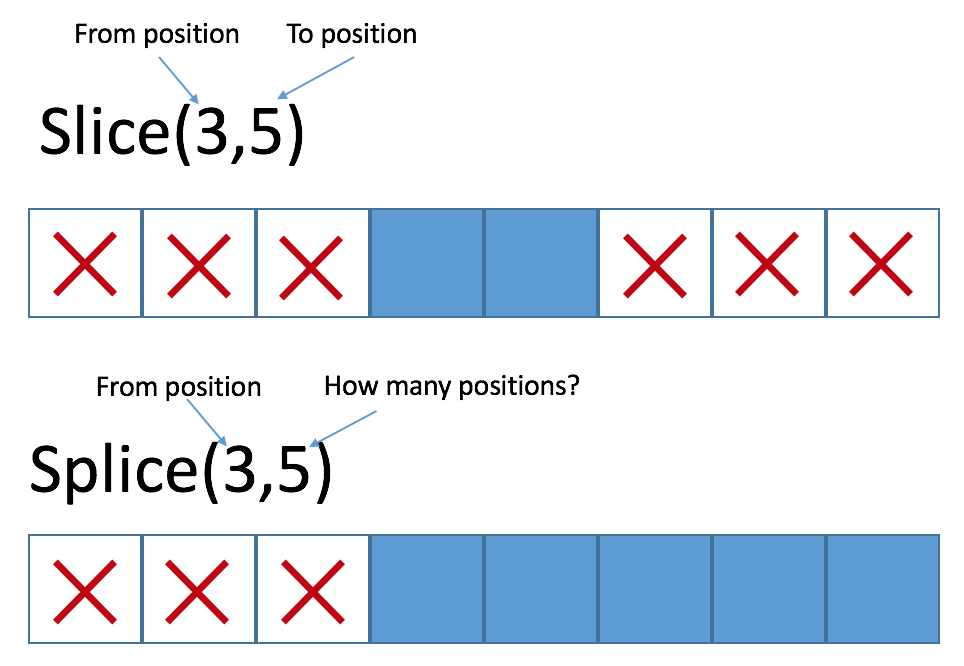
☝ Splice can accept as many optional parameters as wanted and those will substitute the part of the array that has been deleted. The first parameter is the index where the deletion starts, the second is how many elements will be deleted, and from the third onward, the elements inserted after the position set by the first parameter.
Example:
We can use this function to insert elements:
Sorting the Arrays
It is very common needing to sort arrays. For example, sorting a list of students alphabetically by name. You have two functions for sorting in JavaScript, sort() and reverse():
Sort
The sort() function sorts the elements as strings, in alphabetical and ascending order. Which means it works well for strings. But sorting numbers can generate unexpected results:
Sorting Numbers
If you want to sort real numbers, or if you want to use any other type of sorting to sort arrays, you can use a simple "compare function" as a parameter.
You have to define a function that will take care of the comparisons. The sort function will call your function on each comparison and will let your function decide who comes first between both of the elements that are being compared.
When comparing 100 and 200, sort() calls the function we defined: function(100,200) and returns a negative value (-100). Placing "a" (100) before "b" (200). If our function returns a positive value, sort() would place "b" before "a."
Note: This is just one of the uses of the
compareFunctionparameter. You can create custom functions and input them as parameters for any kind of sorting that you need. For more of it, read the docs.
Sorting objects
Now that we know about the compare function, we can use it to tell the sort function how to sort our own special objects, like here for example:
reverse
The reverse() function reverses the order of an array, so if you want a reversed sorted array just make sure to use the sort() function before you reverse the array.