penetration testing
cybersecurity
Use of Port Scanning Tools and Services for pentesting
What is Port Scanning?
Port scanning is a process by which, through specialized tools, the ports of a computer system are analyzed. By scanning ports it is possible to obtain information such as which ports are open, which are closed, or which are protected by firewalls.
This procedure can be used for different purposes. For example, system administrators use it to find out what services are being offered by the machine or to analyze the status of ports and detect and remedy possible vulnerabilities.
However, as we will see later, open port scanning can also be used for unethical purposes. Just as network administrators can use it to detect and fix vulnerabilities, cybercriminals can use it to exploit such security holes.
Port Scanning Techniques
The following are the most common port scanning techniques.
- TCP connect() scanning: This is one of the most common TCP scanning techniques and has the advantage that it is a very fast method and requires very few privileges. It consists of using the
connect()system call. If a connection is established, the port is open; if no connection is established, the port is closed. - TCP SYN scanning: This method is often referred to as "half-open". In reality, a complete TCP connection is not created. Instead, SYN packets are sent as if a connection is to be established. If a SYN-ACK is received in response, the port is open, but if an RST is received, the port is closed. The main drawback of this method is that ROOT privileges are required to perform it.
- TCP FIN scanning: is a port scanning technique that allows you to penetrate systems where firewalls or packet filters could detect the use of SYN packets. Using SYN packets, the response may be an RST if the port is closed, and if it is open the system does not give a response. With FIN packets, this does not happen.
- Fragmentation scanning: This is not a port scanning method per se, but is based on a modification of previous techniques. It consists of splitting or fragmenting the SYN or FIN packets that are sent so that they are not detected by firewalls or packet filterers.
- TCP reverse ident scanning: Thanks to the "ident" protocol, it is possible to know the username and the owner of the services being used within a TCP connection. To do this, a complete TCP connection must be established.
- UDP ICMP port unreachable scanning: This technique differs from the previous ones in that it is not based on the TCP protocol, but uses UDP. This protocol, although usually simpler, is more complex when scanning ports, so the process can become significantly slower.
Is Port Scanning Always Legal?
No, port scanning is not always legal. Port scanning can be used for legitimate purposes. For example, for network and system administrators to check the status of ports, connections, and programs or applications being offered by the computer. It can also be used as a method for scanning for vulnerabilities and security breaches. Administrators can scan ports to create a map of connections and detect possible flaws or vulnerabilities. Therefore, it can be said that port scanning is completely legal, as long as you have permission to access the computer, and it is done for legitimate purposes.
However, it can also be used for unethical purposes. Many attackers employ such techniques to take advantage of these security flaws. In the end, open ports can function as a gateway to a computer, and then perform other malicious activities, such as denial of service attacks.
Port Scanning attacks. What They Are and How to Avoid Them
Following on from the previous point, port scanning attacks are one of the most common methods used by crackers to discover vulnerabilities in a system. The first thing a cybercriminal will do before launching his attack will be a portscan, which will allow him to find out information such as the network architecture, and the services offered on our computers and, of course, to look for holes or security breaches in them. In other words, each open port is a potential gateway to the computer, so it is necessary to take certain security measures.
One of them is not to open more ports than necessary. Normally, the computers already come with a series of predetermined open ports to be able to offer the services and basic functions. It is also advisable to use a firewall or packet filter, which acts as a barrier to protect the computer from intruders. Another recommendation is to always keep computers and systems updated to the latest version since developers usually create patches to correct possible vulnerabilities.
Finally, there is the option of using tools such as PortScanDetector, which allows us to detect when our ports are being scanned. It alerts administrators in cases where more than 10 ports have been scanned, which may indicate that a hacker is trying to access the computer.
Port and service scanning is a common practice in penetration testing and security assessments to identify active services, open ports, and potential vulnerabilities in a system. Here are general steps and some common tools used to perform this type of scan:
General Steps:
- Define the Scope: Establish the scope of the test, identifying the specific systems or networks to be scanned and obtaining the owner's consent.
- Select Appropriate Tools: Choose port and service scanning tools that fit the project requirements and the environment to be evaluated.
- Configure Parameters: Configure scan tool parameters, such as IP address range, port range, and specific scan options.
- Perform Scan: Run the scan tool to identify open ports and services on the target systems.
- Analyze Results: Review scan results to identify services, software versions, and possible vulnerabilities associated with the ports found.
- Log and Document: Maintain detailed records of scan results, including identified services, versions, and any relevant findings.
Common Port and Service Scanning Tools
Nmap: Versatile port scanning and network mapping tool.
Example of Use:
1nmap -p 1-1000 192.168.1.1
Masscan: High performance port scanner.
Example of use:
1masscan -p1-65535 192.168.1.1
Unicornscan: Network and port scanning tool with a focus on speed and efficiency.
Usage Example:
1unicornscan -mU -Iv 192.168.1.1:a
Hping3: Advanced packet forwarding tool, useful for port scanning.
Example of Use:
1hping3 -S -p 80 192.168.1.1
Netcat (nc): Network utility tool that can be used to scan ports.
Example of use:
1nc -zv 192.168.1.1 1 1-100
It is essential to remember that port and service scanning must be carried out ethically and legally, with the explicit consent of the owner of the target system or network.
Reconnaissance and Enumeration With Nmap
Nmap is a completely free and open source utility that allows us to discover networks and hosts, as well as perform security auditing. This program is compatible with Linux, Windows, and also macOS operating systems, but in all of them, it is used through the command line, although we have the possibility of installing ZenMap which is the graphical utility of Nmap to make port scans through the graphical user interface. If you do not want to fight with commands through the console, this GUI could be useful for the first steps with this great program, however, when you have more experience you will surely execute all the commands directly from the terminal.
Nmap allows us to detect hosts on a local network, and also over the Internet, in this way, we can know if those hosts (computers, servers, routers, switches, IoT devices) are currently connected to the Internet or to the local network. This tool also allows you to perform a port scan to different hosts, see what services we have active on those hosts because it will tell us the status of their ports, we can know what operating system is using a particular computer, and can even automate different pentesting tests to check the security of the equipment.
Nmap has different types of port scanning, they can be through TCP segments, UDP datagrams, or ICMP packets, in addition, it allows you to perform scans in a hidden way so that they are difficult to detect by firewalls. Of course, you can perform port scans on specific ports, between port ranges, IP address ranges, and the possibility to use TCP null, FIN, Xmas, and ACK packets as well as SYN, to locate open TCP ports.
Other features provided by this tool are the possibility to make a complete network inventory, and even check if a certain host or service is still up and running. This program was designed to scan many hosts, so if you need to scan multiple targets, you won't have any problems. This program is very flexible, it incorporates dozens of advanced techniques for scanning hosts and ports, in addition, it also allows you to perform audits through NSE (Nmap Search Engine), so it is really powerful.
👉 Nmap has several port states that will appear when doing a port scan. It is critical to know what each Nmap state means because with any port scan, it will return different states.
Principal uses of Nmap
As you can see, Nmap is a very versatile tool. It can be used for a variety of tasks, mostly related to information security. But it also allows us to perform network administration. Some of the most common uses for Nmap are:
- Port scanning: It can be used to perform open port scanning on the network. This gives us the chance to identify possible points where an attacker can attack our network. You can also perform scans of specific ports or a range of ports. This tells us which ports are open, and as such, are likely to be attacked.
- System detection: Nmap can be used to find active systems on a network. This can include servers and network devices. This is done by scanning an IP address, or a range of addresses, to identify devices on the network.
- Service detection: With Nmap it is possible to detect the services that are running on the network, which helps us in many cases to detect vulnerabilities. We will be able to identify services such as HTTP, Telnet, FTP, SSH, among many others. This allows us to provide very detailed information about the software being executed, including their versions.
- Network mapping: can be used to map networks. This can include various factors such as the location of a device or the topology of the network itself. This will make it much easier to create a visual map of the entire infrastructure, identifying the devices and how they are connected.
- Security testing: With Nmap you can perform penetration tests and security assessments. This allows us to identify vulnerabilities in the systems or network. This is directly linked to port scanning.
- Monitoring: Nmap can monitor the availability of servers or network devices. This helps us to see if they are working properly.
What to Scan Ports For
As we have seen, with Nmap we have a tool that specializes in scanning the ports of computer systems, obtaining information about whether they are open, closed, or protected with firewalls. This can be done for a multitude of purposes, such as knowing what services are being offered from a computer by administrators or for security, looking to solve a problem that may come in the form of a vulnerability.
But this can also be used for malicious purposes. Just as administrators can analyze them to look for possible vulnerabilities, an attacker can do it for the same reason, but to take advantage of it to infiltrate the network by exploiting a security breach.
Port status with Nmap.
- Open: An application is actively accepting TCP or UDP connections. The port is open and can be used, pentesters will be able to use this open port to exploit the system. This is the default state if there is no firewall blocking access.
- Closed: A port that is closed is accessible because it responds to Nmap, however, there is no application running on that port. It is useful to discover that a host is up, or as part of the detection of an operating system. For the system administrator, it is advisable to filter these ports with the firewall so that they are not accessible. For the pentester, it is advisable to leave these ports "closed" for later analysis, in case a new service is set up.
- Filtered: In this state, Nmap cannot determine if the port is open because there is a firewall filtering Nmap packets on that port. These filtered ports are the ones that will appear when a firewall is enabled. Nmap will try several times to try to connect, which makes port scanning quite slow.
- Open/Filtered: Nmap does not know if the port is open or filtered. This occurs because the open port does not send any response, and the lack of response could be due to the firewall. This state appears when using UDP and IP, and we use FIN, NULL, and Xmas scans.
- Closed/Filtered: in this state, it is not known if the port is closed or filtered. Only this state is used in the IP Idle Scan.
Effectiveness of Nmap
Nmap is a tool that is considered to be highly effective. This is due to a combination of functionality and advanced features, which makes this solution one of the best we can find. It can perform vulnerability scans to identify possible weaknesses in security system configurations. Therefore, if it were not effective, it would not be such a well-known tool. Therefore, we could say that Nmap's fame is a good indicator of the quality that it can provide in a wide variety of different situations.
On the other hand, beyond its effectiveness in identifying devices, services, and vulnerabilities, is its ability to work with different network protocols. Among others, TCP, UDP, ICMP, and IP. All of which can be integrated with other security and analysis tools. These can be tools such as Metasploit or even Wireshark. This makes Nmap a very versatile tool for all types of systems.
Instead, this is not a perfect solution, nor does it represent a security measure against problems. Although it is very effective and powerful, it requires some knowledge on the part of the users who use it. As well as the availability of the necessary skills to use it with all the guarantees, and taking advantage of its performance and functions to the maximum. We must also think that many devices may have some kind of protection against scans by applications such as Nmap, or may even be difficult to detect. But in these cases, it would no longer be a problem of the efficiency of Nmap or its functions, but of the protection measures set up on those devices. In any case, if we are looking for an effective, reliable solution with a good track record, Nmap is one of the best solutions at the moment.
Customization of NMAP
As you can see, NMAP is an open source tool, so it is highly customizable. This makes it a highly adaptable solution to the needs of each user, in all kinds of scenarios. But this is something that is not done lightly, but some factors stand out above others. Starting with the scanning options, where the range of options is very wide. This allows you to manage many parameters and advanced options, which completely modify the operation of NMAP. Customized scanning allows us to have very valuable information of all kinds when performing port analysis, for example.
On the other hand, there are the NSE (Nmap Scripting Engine) scripts. This is one of the most powerful features of NMAP, which allows you to run highly customized scripts during scan time. Since we can create the scripts ourselves, they can be as complex as necessary. And as such it gives us that added customization, which we would not have without this section of NMAP. Everything is done by looking at custom output data, where you can set many parameters. From the output format, generate HTML reports, and the results that we will need to include the analysis that is performed on the network.
Finally, NMAP has a great capacity for integration with other tools. One of the most striking features is the ability to set NMAP as an input for other security tools we use, or even for intrusion detection. Which, again, can be combined with the scripts we mentioned previously. Now that we've seen the main features of Nmap and the port status we have available, let's install and use it.
Download and install Nmap on any System
The first thing we need to do to use this powerful program is to download and install it. In the Nmap download section you can find all the links, binaries, and source code for installation on Windows, Linux, and MacOS operating systems. This program is currently available in all Linux-based operating system repositories, so its installation is really easy. In Kali Linux is already installed, but if your Linux is not installed simply run the installation command followed by "nmap", and you will install the program without difficulties.
1sudo apt install nmap
Examples of Nmap usage
Nmap is a very advanced and complex program, with dozens of commands and attacks that we will be able to perform, to discover all the hosts that we have in a local home or professional network, in addition, it is also able to detect hosts on the Internet, that is, we will be able to scan one by one any IP address on the Internet and public subnets.
Once we have discovered that the host is online, we can perform a quick port scan and check if it has a firewall filtering all packets, or if we have an open port to exploit a vulnerability. Nmap allows you to use both private and public IPv4 addresses, as well as IPv6 addresses, to scan the ports of any host.
Next, we will see some examples of how to use Nmap at the user level, and also with more advanced commands, this program will allow us to discover with some accuracy what operating system is using the remote host, ideal to get as much information as possible.
Quick Port Scan
If you want to perform a quick port scan on a specific host, type the following command. This basic command will be in charge of scanning the main ports to the defined private or public IP address, a very important detail is that it will not scan all ports, but the most commonly used ones.
1nmap [ip]
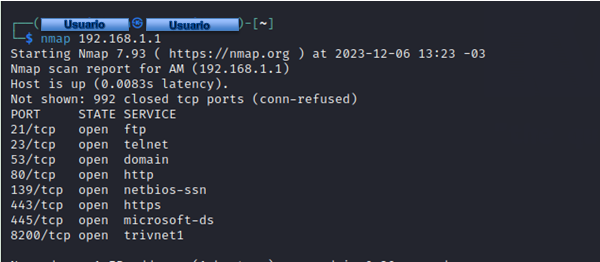
For example, if we want to perform a quick scan of the main ports to a host with IP address 192.168.1.1, the command would be as follows:
1nmap 192.168.1.1
The program will return the ports that are open on the target machine.
In the case of wanting to scan every one of the ports we will have to resort to the following command and put a range from port 1 to 65535, in this way, we will be checking if every one of the ports is open, closed, or filtered.
Perform a Scan of a Range of Ports
Instead of performing a scan of all ports, we can set a range of ports to check. To do this, we will run:
1> nmap -p [range] [ip]
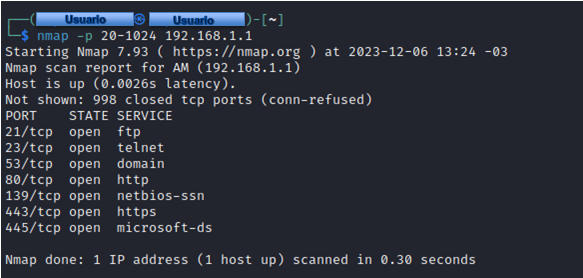
If we want to perform a port scan from 20 TCP to 200 TCP on the IP address 192.168.1.1, just run the following command:
1nmap -p 20-200 192.168.1.1.1
The program will indicate which ports are open within that range.
Depending on the latency of the connection between your computer and the remote host, and also the number of ports to be scanned, this process could take from several seconds to about 10 minutes.
Detect the operating system and more host data
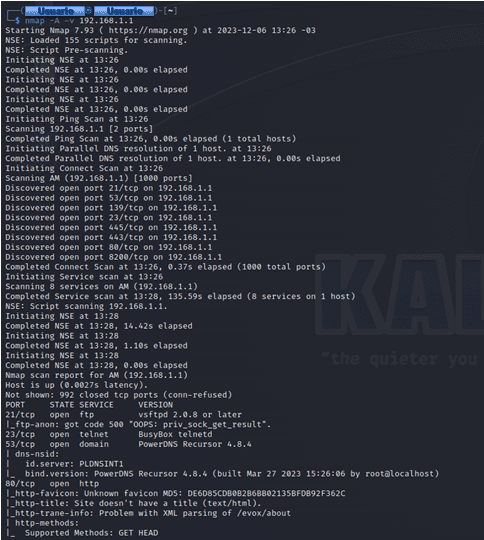
We can instruct Nmap to detect the operating system. It does this by sending packets and analyzing the way it sends them back, being on each system differently. Along with this, it will perform a scan of ports and services for vulnerabilities. Also, the scan will return useful information. To do this, we must run:
1nmap -A -v [ip]
If we want to perform this scan to the IP address 192.168.1.1 we can run the following command:
1nmap -A -v 192.168.1.1
This operating system detection test is not completely reliable because it depends on many parameters, in some cases the accuracy is very good, especially in differentiating whether it is Windows or Linux, but within the Linux world, it is complicated to know which operating system it is in particular.
List of all the commands
This program is complete, so far we have used the basic commands to discover hosts and also to see if you have the ports open, however, this does not stay like that, and we have a great list of commands to squeeze the most out of this tool.
Select targets
IP addresses or ranges, system names, networks, etc.
- Example: scanme.nmap.org, microsoft.com/24, 192.168.0.1, 10.0.0-255.1-254
- iL file list in file -iR n choose targets randomly, 0 never ends
- -exclude -excludeefile file exclude systems from file.
Discover Systems
- PS n tcp syn ping
- PA n ping TCP ACK
- PU n ping UDP
- PM Netmask Req
- PP Timestamp Req
- PE Echo Req
- sL List scan
- PO ping per protocol
- PN Do not ping
- N Do not do DNS
- R Resolve DNS on all target systems
- -traceroute: traceroute to the system (for network topologies)
- sP perform ping, same as -PP -PM -PS443 -PA80
Port Scanning Techniques
Most of the time, when users are just starting to use this tool, they will most likely try the resolution of most problems with the SYN scan type because it is one of the most versatile. But, as they progress and get to know the tool in depth, they will realize that they will expand their range of solutions, and here below we explain a little bit some of the commands that are most useful when scanning ports.
- sS analysis using TCP SYN: This type of scanning is based on scanning speed, hence the versatility mentioned above, as it allows you to scan thousands of ports per second on a network that is unprotected or lacks a firewall. In addition, in terms of privacy, it is an excellent technique, since it does not complete TCP connections and therefore does not attract attention.
- sT analysis using TCP CONNECT: This type of scanning, we could say that it is the one that is mainly used, especially when we can not run a SYN scan, this type of connection analysis, what it does is to make or issue a call to the connection system to establish a connection to the network we are analyzing. Then, Nmap what it does is to use this call to analyze the information about each connection attempt, the main disadvantage of this type of analysis is that it takes us a little longer to identify the ports that are open than it would take us for example with the SYN.
- Your analysis using UDP: This type of scanning is quite simple, it is mostly used when we want to keep track of ports such as DNS, SNMP, and DHCP on our network. Of course, being simple does not take away from the fact that these are quite important ports, as they are usually the areas where attackers are looking for vulnerabilities to exploit.
- sY analysis using SCTP INIT
- sZ using SCTP COOKIE ECHO
- **IP protocol
- sW TCP window -sN
- -sF -sX NULL, FIN, XMAS
- -sA TCP ACK
Ports to be Scanned and Scan Order
- p n-m range
- p- all ports
- p n,m,z specified
- p U:n-m,z T:n,m U for UDP, T for TCP
- F fast, all 100 common
- -top-ports n analyze the most used ports
- r non-random
Duration and Execution
- T0 paranoid
- T1 stealthy
- T2 sophisticated
- T3 normal
- T4 aggressive
- T5 insane
- -min-hostgroup
- -max-hostgroup
- -min-rate
- -max-rate
- -min-parallelism
- -max-parallelism
- -min-rtt-timeout
- -max-rtt-timeout
- -initial-rtt-timeout
- -max-retries
- -host-timeout -scan-delay
Service and version detection:
- sV: services version detection
- -all-ports do not exclude ports
- -version-all test each scan
- -versiontrace track version scanning activity
- O enable OS detection
- -fuzzy guess OS detection
- -max-os-tries set the maximum number of attempts against the target system
Firewall/IDS bypass
- f fragment packets
- D d1,d2 mask decoy analysis
- S ip spoof source address
- -g source spoof source port
- -randomize-hosts order
- -spoof-mac mac change source MAC
Detail and debug level parameters
- v increase the level of detail
- -reason motifs per system and port
- d (1-9) set level of debugging
- -packet-trace packet path
Other options
- -resume file continue aborted analysis (taking output formats with -oN or -oG).
- 6 enable IPV6 analysis.
- A aggressive, same as with -O -sV -sC -traceroute.
Interactive options
- v/V increase/decrease scan detail level.
- d/D increase/decrease debugging level.
- p/P enable/disable packet tracing.
Scripts
- sC perform analysis with default scripts.
- -script file execute script (or all).
- -script-args n=v provide arguments.
- -script-trace displays incoming and outgoing communication.
Output formats
- oN save in normal format.
- oX save in XML format.
- oG save in format for later use of Grep.
- oA save in all of the above formats.
💡 Mainly these are the commands available in Nmap. Before finishing, we must say that Nmap has a multitude of options with which to perform complete network analysis. We can consult all the available options by typing:
1nmap --help
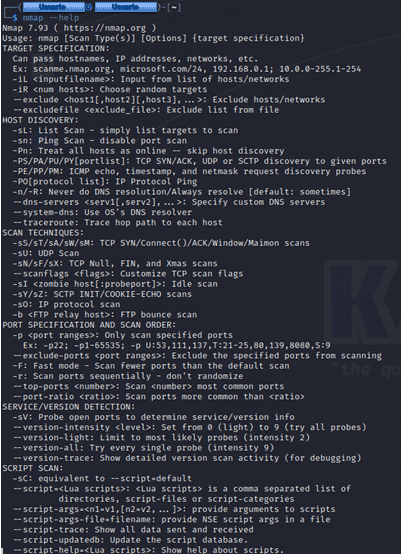
Nmap is undoubtedly a very simple and complete tool to perform network audits, but this does not end here, we also have available Nmap NSE for advanced pentesting.
Other scanning techniques
As we have seen, Nmap offers many parameters to perform a more tailored scan, but there are currently other methods to perform this task which can be interesting. Each of them has its characteristics and can vary in effectiveness.
- TCP connect()scanning: This is one of the most common forms of scanning because it is fast and does not require too many privileges on the computer.
- TCP SYN scanning: Also known as "half-open". This does not create a TCP connection but uses the sending of SYN packets. You can get two different responses, a SYN-ACK indicating that the port is open, and an RST indicating that it is closed.
- TCP FIN scanning: Allows port scans to be performed on systems with firewalls or SYN packet filters.
- Fragmentation Scanning: This is not a scanning as such, but is used to modify the previous techniques by splitting or fragmenting SYN or FIN packets. This is done so that they are not detected by firewalls or packet filters.
- TCP reverse ident scanning: With this identifier, it is possible to know data about the responsible party for the services that are using a given TCP connection. It requires a complete connection.
Thanks to these advanced scanning techniques, we can determine whether ports are open or closed.
Nmap NSE: What Is It, and What Is It For?
Nmap Search Engine also known as Nmap NSE, is a large database with thousands of scripts that will allow us to automate the pentesting of systems and networks. The first step of any pentesting is to perform a port scan, once this port scan is done, we can try to exploit vulnerabilities in the services that are running behind a particular port, for example, we could attack web servers, Samba servers, FTP, SSH servers, DNS servers, check if the different services have known vulnerabilities or directly try to authenticate in them if they have authentication as in FTP or SSH.
NMAP NSE is a set of scripts that will allow us to automate many actions, such as performing brute force attacks on Samba servers, to try to access them and take control, although we could also attack it to perform a denial of service attack and make the service unavailable. The same could be done with FTP servers, SSH servers, and much more, above all, the web servers that must have an open port in the firewall are the ones that must be protected the most to avoid or mitigate the attacks that could be carried out.
For example, if we want to perform a brute force attack, based on a list of users (with a file called users.txt) and with a list of passwords to test (with a file called keys.txt) to an SSH server of a particular computer that has the IP 192.168.25.01, we can put the following command:
1nmap -p 22 --script ssh-brute --script-args userdb=usarios.txt,passdb=claves.txt --script-args ssh-brute.timeout=4s 192.168.25.01
If we want to know if an FTP server has anonymous authentication enabled, we can easily do so by setting the following command:
1nmap -sV -sC -p21 192.168.25.01
If we want to perform a brute force attack on an FTP server to a server with the IP 99.99.99.99.99, we can put the following command:
1nmap -p 21 --script ftp-brute 192.168.25.01
We have a huge amount of scripts within Nmap NSE to check the security of dozens of services because we will not only have the typical Samba, FTP, SSH servers, and more, but we can also attack in a very specific way a web server with special HTTP headers to see if there are vulnerabilities, of course, we will have specific scripts that will allow us to exploit vulnerabilities to the PHP of web servers, of course, we can also exploit vulnerabilities to the different Samba, FTP and SSH servers, that is, known vulnerabilities that have already been fixed, but it is possible that the target still has them operational. For this reason, it is so important to update as soon as possible all the services that we have exposed to the Internet and also services that we have exposed to the local network because malware could exploit a vulnerability and turn the penetration attack into a ransomware attack to encrypt all files and folders.
I recommend visiting the NSE official website where you will find all the scripts currently available in this large database, and you will also get examples of how to use them.
Zenmap, the Graphical Interface to Nmap
Zenmap is a free tool that we can use to scan ports. We can know which ones we have opened, to avoid problems when using some programs or accessing a server. It is the graphical interface of the popular open-source program Nmap, which allows a complete port scan of any connected computer. It should be noted that this completely free tool is available for different operating systems such as Microsoft Windows, Linux, or macOS. Likewise, it allows users to run different types of port scans. It is ideal for both less experienced and more advanced users.
To start using Zenmap the first thing we have to do is download it. We can do it from the official website of Nmap. There we will find the different versions, depending on the operating system we are using. The installation process is simple, fast, and intuitive. In a few seconds, we will have it ready to use.
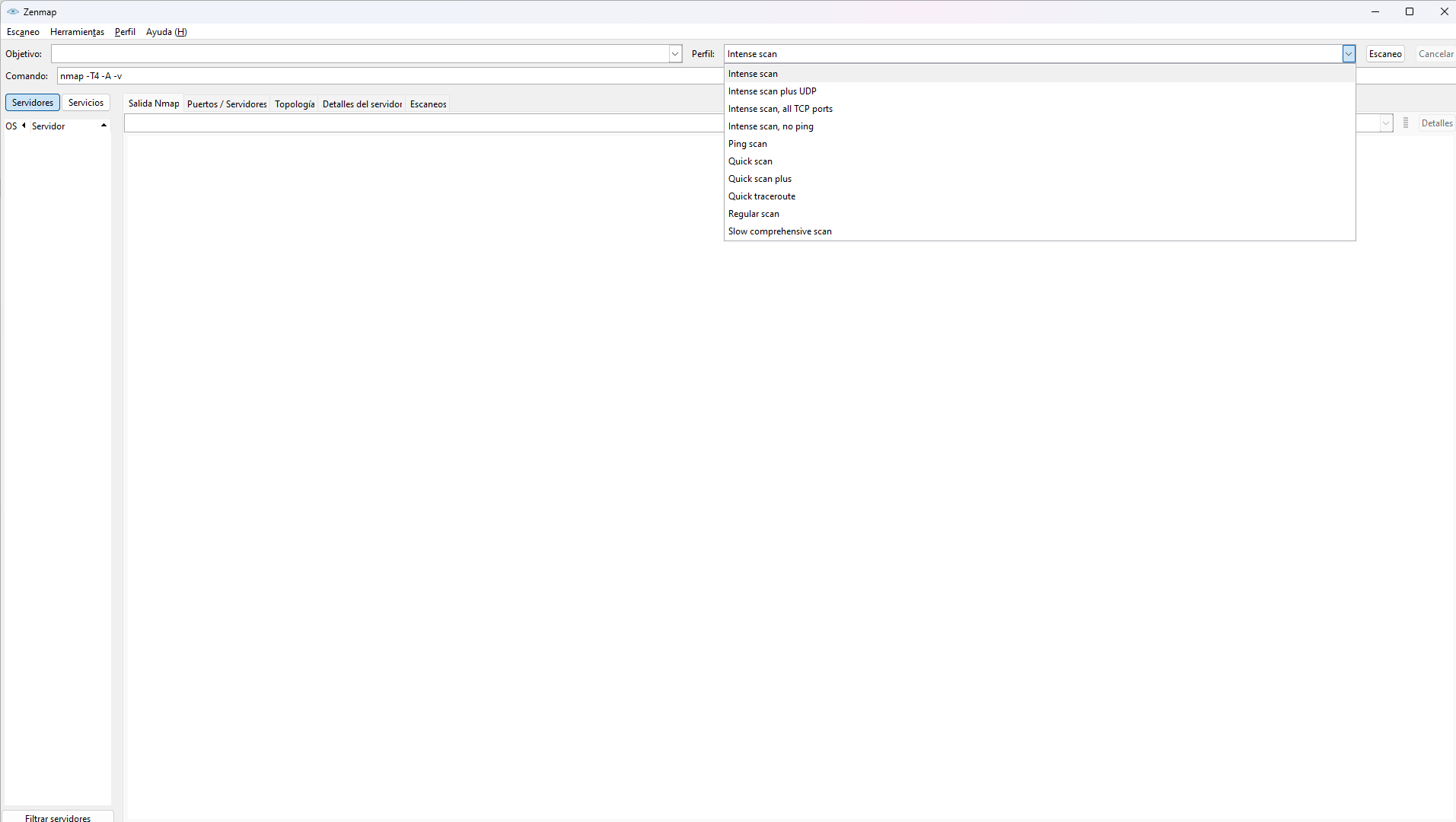
When we have installed it we will simply have to execute it. You will see an image like the one above. We can choose a full port scan, quick scan, TCP ports, UDP ports, etc. With Zenmap we can see which ports are open on any device. In the Target section, we have to put the IP address that corresponds to that computer to subsequently perform the scan to show which ones are open. So the first thing we have to do is to know what is the IP address of our computer.
On Windows, this process is very simple. We simply have to go to Start, run the Command Prompt and then ipconfig. It will show us a series of information, among which we can see the default gateway (usually 192.168.1.1.1) as well as the IP address of that computer. When we know which is the address, we will have to put it in the section of Objective, in Zenmap. Then we will have to choose the type of scan we want to perform, as it could be for example a full scan of all TCP ports.
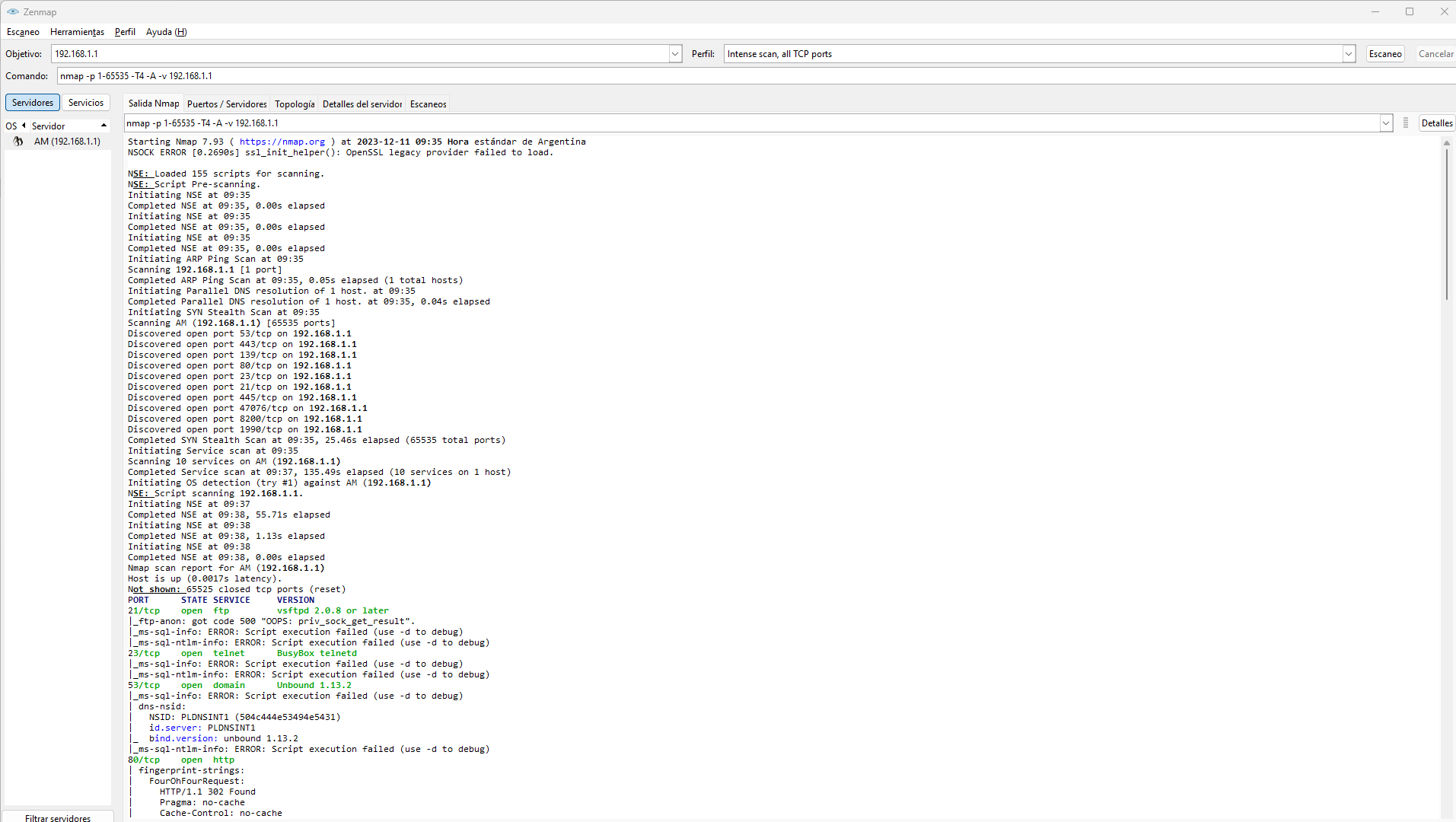
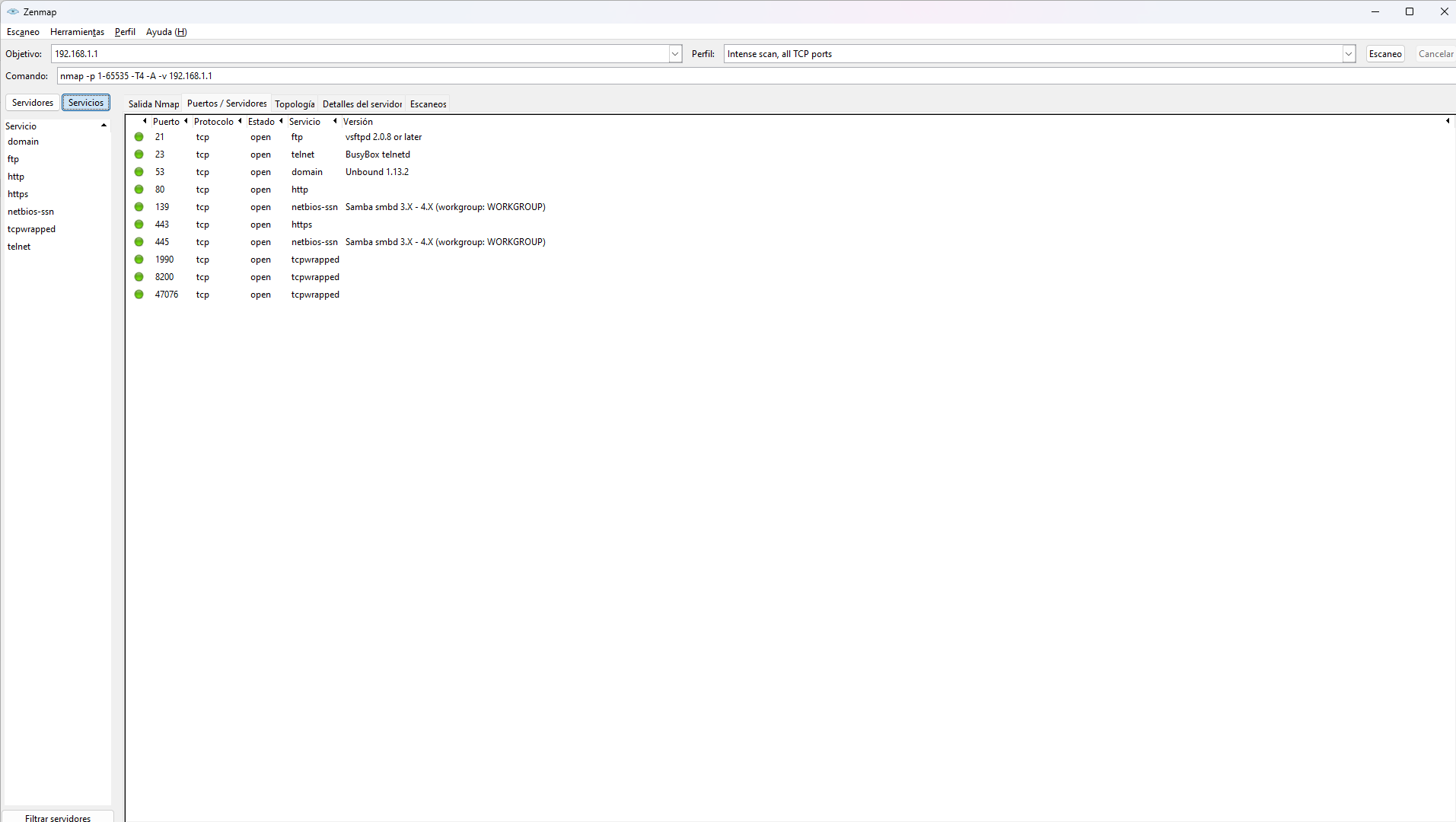
In Zenmap, at the top, we will find different tabs. We will see Nmap Output, Ports/Servers, Topology, Server Details and Scans. All of them provide us with information, as well as being able to choose the type of service on the left side. When we click on Ports/Servers we will see a compilation of all the open and filtered ports on that host. It is necessary to bear in mind that more or less ports will appear depending on the type of scan that we have carried out.
If we click on Scans we will see all the scans we have performed. We can save them to be able to analyze the data on another occasion, as well as to eliminate them so that they do not appear there.
This can be done with any other computer connected to the network. For example, we can also check the open ports and scan our cell phone. We only need to know the IP address. However, keep in mind that this process may take more or less time depending on the type of device.
In short, Zenmap is an interesting program with which we can perform port scans. We can use it on Windows, which is the most widely used operating system on desktop computers, as well as Linux and macOS. Its use is simple and intuitive, and we can have more control over which ports we have opened, especially when we need to know if a computer is going to work properly when using an application that requires certain ports open.
Implementation in companies
Many companies decide to implement these systems to have a little more control over their networks. But this is something that must be studied carefully, and following some steps so that the whole process is efficient. These steps are:
- Needs assessment: Whenever and wherever a new system is implemented in a company, it is necessary to assess the needs that we are going to have within the organization. We will have to identify the objectives, the critical assets of the network, and every one of the security requirements that we will need to solve with NMAP.
- Installation and configuration: In any environment, it is always best to go to the official sites to obtain the tool. This will make the process secure. Once we have it, we will have to correctly configure the settings and options in NMAP so that it complies with the specific requirements.
- Policies and procedures: The policies established in NMAP must be clear and concise. Here we will be able to configure the scans and types, as well as the notification and reporting protocols for findings.
- Training: All personnel using NMAP must be properly trained and qualified to use it. It will be necessary to understand how to use the tool safely and effectively, and that they should always be aware of all policies and procedures.
- Analysis: As usual, NMAP will give us some results. These must be analyzed, and as such it will be necessary to have a procedure for this. This will make the analysis much more effective, and we will have the right information at all times.
- Updates: Once we have the tool installed and configured, we will have to establish how we are going to keep it updated. This is something critical, as it will be necessary for everything to be kept as secure as possible and with the most optimal performance.
👉 As we can see, Nmap is a tremendously useful tool, which can give us many facilities when managing networks.