virtualbox
cybersecurity
What is VirtualBox?
VirtualBox is a free program that allows you to install different operating systems inside your current computer, as if they were independent programs. It's like having several computers in one.
VirtualBox is relatively easy to use, even for people with no computer experience.
What do you need to use VirtualBox?
- A computer with a relatively powerful processor (at least 2 cores) and enough RAM (at least 4 GB).
- Free space on your hard drive to install the operating systems you want to test.
- A primary operating system compatible with VirtualBox (Windows, Linux).
What is a virtual machine (VM)?
Imagine that your computer is like a house...
The host operating system (also called host) is like the owner of the house. It controls everything and allows you to use programs, browse the internet, etc. A virtual machine (also called a guest) is like a room inside the house. In it, you can install a different operating system, as if it were an independent tenant. In other words, a virtual machine is a program that allows you to run another operating system inside your current operating system. It is like having two computers in one.
What is a virtual machine for?
- To test new operating systems without risk: You can install a different operating system in a virtual "room" and test it without affecting your main operating system. If you don't like it, you can easily remove it.
- Learn about different operating systems: You can use a virtual machine to practice with different operating systems and learn how they work.
- Run programs that only work on a specific operating system: If you need to use a program that only works on Windows, for example, you can install it in a Windows virtual machine inside your Mac or Linux.
- Isolate insecure software: You can install untrusted software in a virtual machine to prevent it from affecting your main operating system.
VM resource management
In VirtualBox, resource management for virtual machines is based on the configuration of the following items. These can be assigned at the time of creating a new machine and can be modified later if necessary.
RAM memory
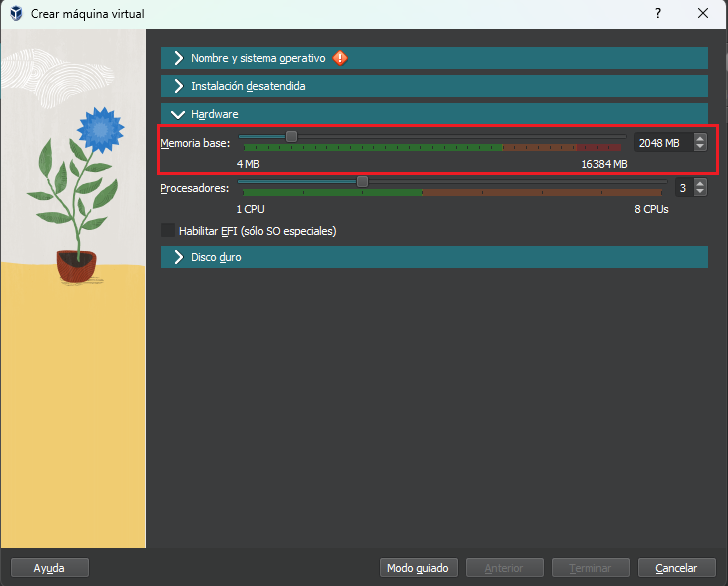
Determines how memory is allocated to the virtual machine. The value assigned will be the one available for the guest machine to use to operate.
It can be determined when the machine is created:
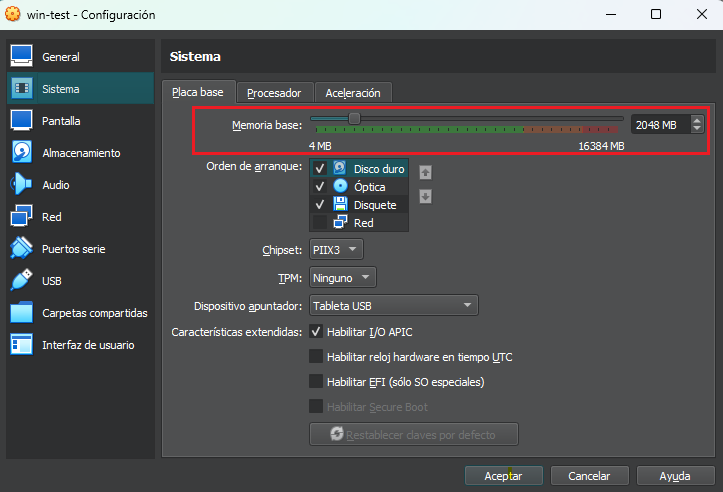
Or it can be changed after the machine has been created, but can only be changed while the guest is turned off.
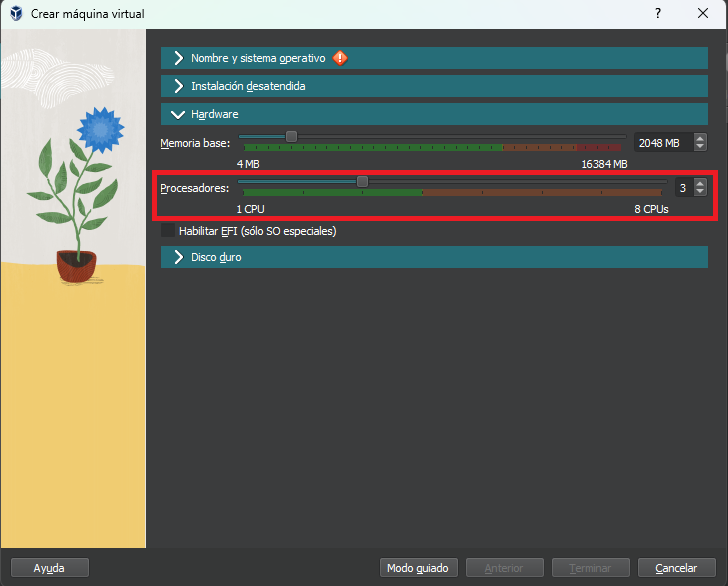
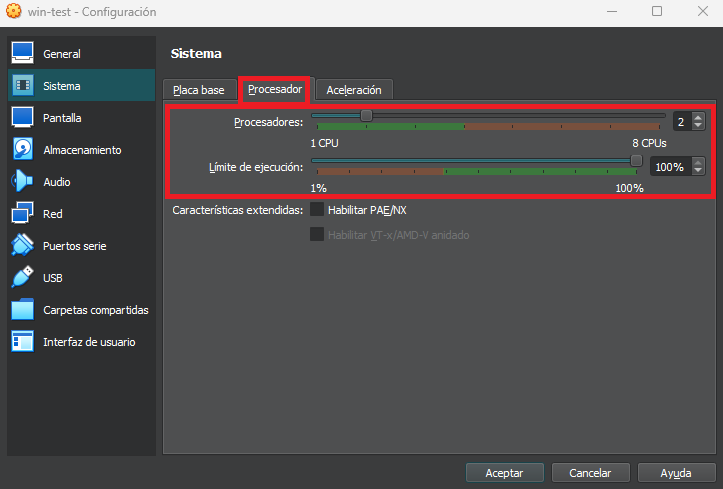
CPU
In this section you assign the number of processors that can be used by the virtual machine. The number of processors available to assign corresponds to the logical processors that the host has, for example: With a processor with 4 cores and 8 threads, 8 processors are available.
Once the machine is created you can also modify the guest processors, and you can even limit the percentage of the host processor that you will be allowed to use.
Storage and virtual media
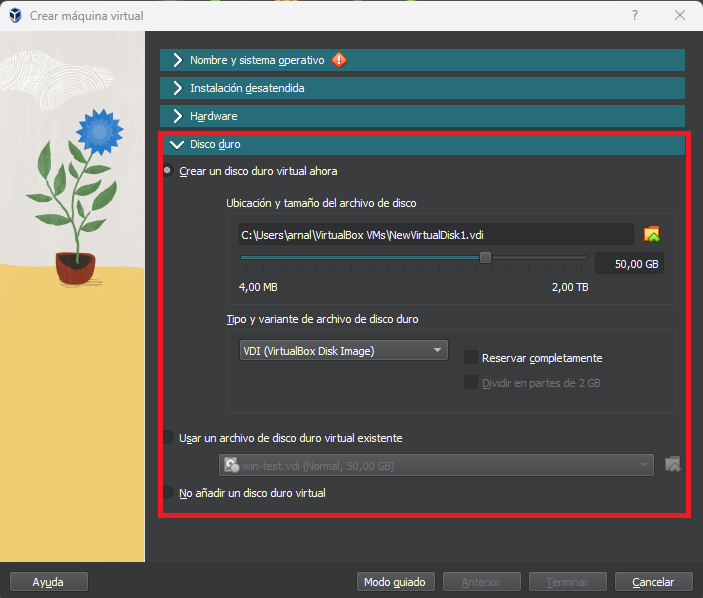
The host operating system is hosted on a virtual hard disk, which is a file that simulates a physical hard disk for the virtual machine, and is also portable (it can be easily moved to another machine) and also compresses the data to save storage space on the host.
When the machine is created, the name of the file and the maximum capacity of the virtual hard disk are determined. The file will grow as the host has more and more data, until it reaches its maximum capacity. In the same way, pre-existing disks can be added to a virtual machine.
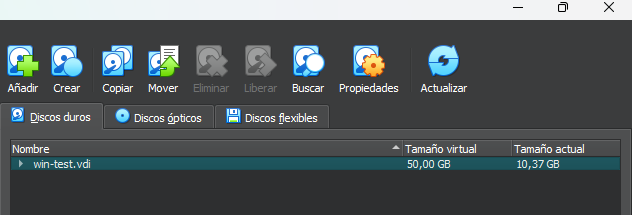
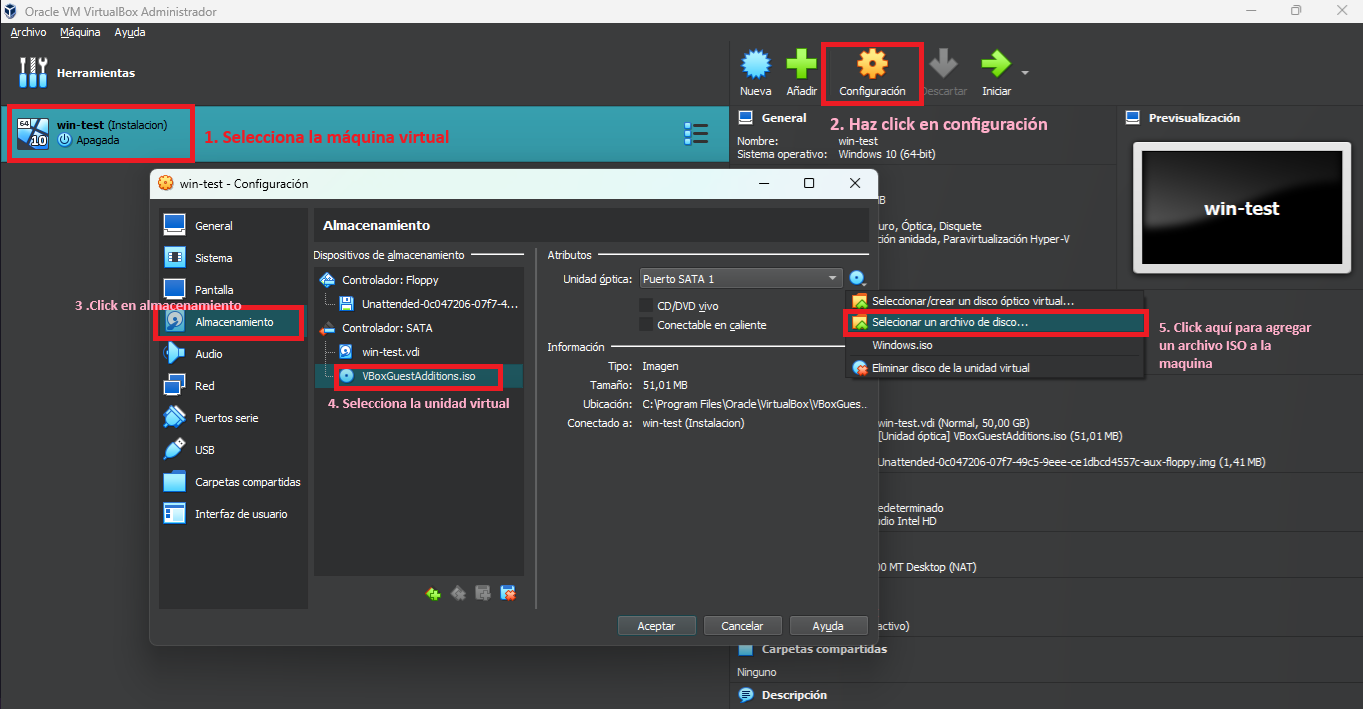
Once created the machine with its respective disk, we will be able to see and modify the virtual units in the "Virtual Media Manager". This tool shows us all the virtual hard disks, the Virtual Disk Drives. In each of its tabs we will have options to import new virtual media or import some that already exists, in this way we can configure virtual machines with any type of connected media to simulate the necessary environment.
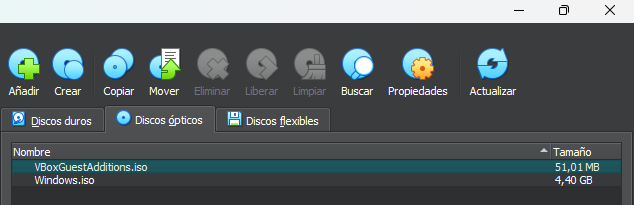
Regarding optical media, these are comprised of ISO files that can be downloaded from various sources and added to virtual machines. These files are the most commonly used standard for operating system installers, both Windows and GNU/Linux systems, both available from their respective official websites. Using the "Add" option in the "Optical Discs" tab.
Network
- Network adapter type: Determines how the virtual machine connects to the network.
- Network Mode: Determines how the virtual machine interacts with the host network.
Other resources
- USB devices: You can connect USB devices to the virtual machine.
- Sound: You can configure the sound output of the virtual machine.
- Shared folders: You can share folders between the virtual machine and the host operating system.
To manage the resources of a virtual machine in VirtualBox:
- Open VirtualBox and select the virtual machine you want to configure.
- Click on "Settings".
- Select the resources tab you want to configure (memory, CPU, storage, network, etc.).
- Modify the configuration values according to your needs.
- Click "OK" to save your changes.
Tips for managing the resources of a virtual machine:
- Allocate the amount of RAM and CPU the virtual machine needs for optimal operation without compromising host performance. If you allocate too much RAM or CPU, the host operating system may slow down.
- Use an appropriately sized virtual hard disk. If the virtual hard disk is too small, the virtual machine may run out of disk space.
- Configure the right type of network adapter for the virtual machine and the environment you are trying to simulate, you may need to have several network connections.
- Share folders between the virtual machine and the host operating system only if necessary.
It is important to note that the amount of resources you can allocate to a virtual machine is limited by the resources available on the host operating system.