Introduction to cybersecurity
Cybersecurity encompasses a series of practices that are often confused with hacking, so let's clear up any doubts. Cybersecurity is a set of interdisciplinary practices that includes information security, data security, privacy, secure infrastructure, policies and regulations, and, of course, hacking. In other words, cybersecurity is the universe in which all these practices are possible. Each discipline mentioned above is a planet in this vast universe called cybersecurity.
Cybersecurity is often mistakenly confused with hacking, and hacking is indeed part of cybersecurity. However, cybersecurity is a box full of multiple disciplines, as mentioned above. Therefore, a cybersecurity professional can play various roles such as SOC Analyst, pentester, cybersecurity analyst, system administrator, malware analyst, and risk analyst, among others.
Why is cybersecurity important in a company?
Companies issue invoices for thousands or millions of dollars every day. Imagine you are a sales executive, you arrive at the office one day, and... the company is under attack! The company you work for has fallen victim to cybercriminals, and now you have no access to the sales system. How much money do you think is lost daily while this attack is ongoing? How many customers could you lose? How many sales could be affected? How much information about customers, suppliers, and employees could be compromised? Answering these questions reveals the value of cybersecurity in a company. The primary asset of a company is its information; information is everything! Information enables process execution, communication, sales, and much more.
By implementing a cybersecurity culture in companies, we can achieve:
- Protection of sensitive data: Companies handle a large amount of confidential data, such as financial information, customer data, trade secrets, and intellectual property. Lack of security could jeopardize these critical assets, resulting in financial losses, damage to reputation, and legal sanctions.
- Regulatory compliance: Many sectors and jurisdictions have strict regulations regarding data protection and customer privacy. Companies that do not comply with these regulations may face significant fines and other legal issues. Effective cybersecurity is essential to ensure regulatory compliance.
- Business continuity: Cyber threats, such as ransomware attacks, can cripple a company's operations. This can result in revenue loss, service disruption, and damage to customer relationships. Cybersecurity helps ensure business continuity by minimizing the impact of such incidents.
- Reputation protection: A security breach can damage a company's reputation and customer trust. Consumers are increasingly aware of the importance of their data security and may avoid doing business with companies that do not take adequate measures to protect information.
- Financial costs: Recovering from a cyber attack can be expensive. This includes not only the direct costs of mitigation and recovery but also indirect costs related to revenue loss and investment in security after the incident.
- Constantly evolving threats: Cybercriminals are continually evolving, developing new techniques and tools to bypass traditional defenses. Staying up-to-date with these threats requires continuous investment in cybersecurity.
- Supply chain protection: Companies often rely on suppliers and business partners for their operations. Lack of security in the supply chain can expose the company to additional risks. Cybersecurity helps protect the entire network of business relationships.
- Organizational resilience: Cybersecurity is not just about preventing attacks, but also about having the ability to respond and recover quickly when incidents occur. This includes incident response planning and the implementation of recovery measures.
👉 Cybersecurity is essential to protect its assets, ensure customer trust, comply with regulations, maintain business continuity, and avoid significant costs associated with potential cyber-attacks. It is a critical investment in today's digital age.
The Three Pillars of Cybersecurity
In cybersecurity, there are three pillars: Confidentiality, Availability, and Integrity. Your duty as a professional is to protect these pillars as a very valuable asset.
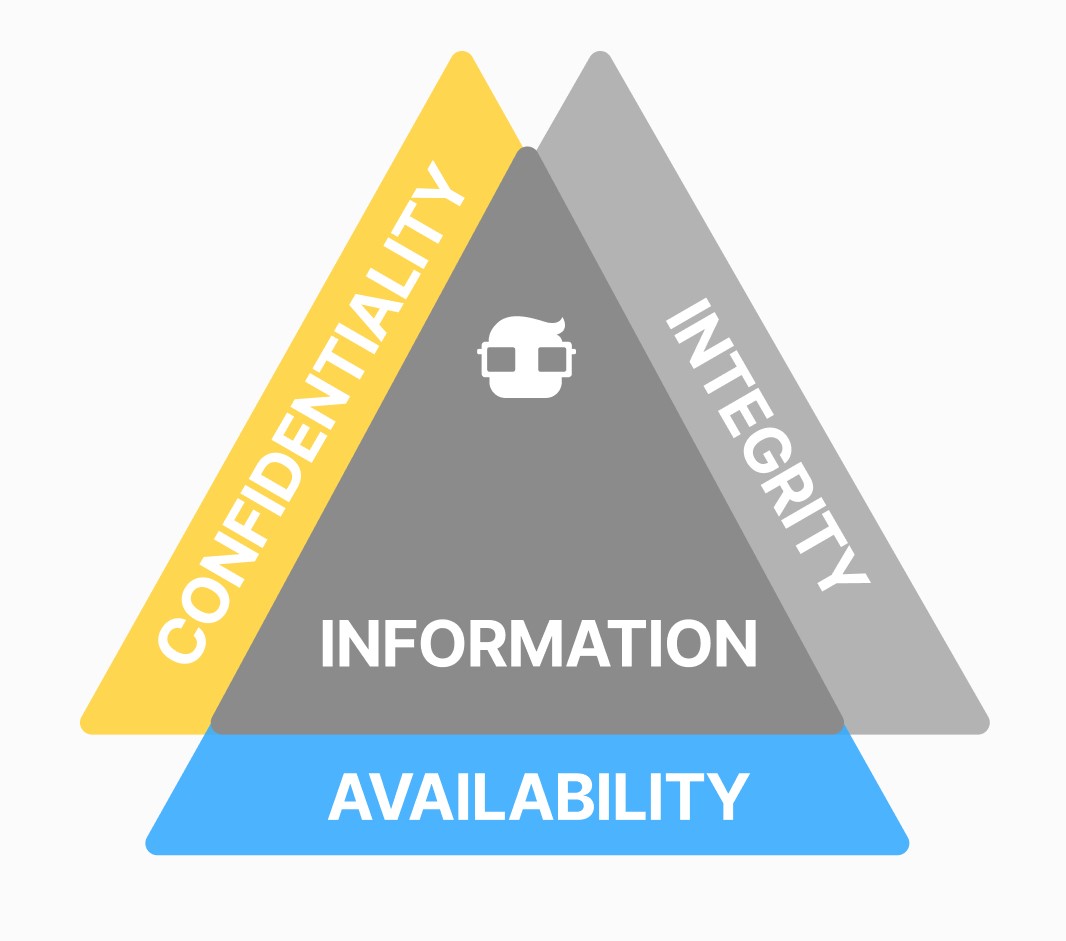
-
Confidentiality:
- Confidentiality refers to the ability to protect information so that only authorized individuals can access it. This means that confidential information should not be within reach of unauthorized individuals or external entities.
- Confidentiality is achieved through the use of techniques such as data encryption, user authentication, and access management. The goal is to ensure that only those who have permission to view certain data can do so, keeping the data secure and protecting privacy.
- Confidentiality ensures that information is only available to those who need it. For example, if you are a sales executive, you need information about products and customers, but you do not need information about server versions and configurations. Confidentiality ensures that each person receives the correct information to avoid information leaks that could compromise the company and perpetuate a cyber attack.
-
Availability:
- Availability refers to ensuring that information and resources are available and accessible when needed. This means that critical systems and data must be available for use at all times without unplanned interruptions.
- To ensure availability, security measures, and disaster recovery plans are implemented to prevent and mitigate disruptions, such as cyber-attacks, hardware failures, natural disasters, etc.
-
Integrity:
- Integrity relates to the accuracy and reliability of information. It refers to ensuring that data has not been altered unauthorized and remains accurate and complete.
- To protect data integrity, techniques such as change control, digital signatures, and audit logs are used. These measures help detect and prevent unauthorized modifications to data, which could lead to incorrect decisions or actions.
Confidentiality, availability, and integrity form a robust framework for information security. These principles guide the implementation of policies, procedures, and security technologies that help protect an organization's information assets and maintain the trust of customers and stakeholders. Additionally, they are essential for complying with privacy and data security regulations in various industries and jurisdictions.
What can they do with my data?
Data identifies you as a unique individual. You are the only person in the world with your fingerprints (biometric data), the numbers on your bank card are also unique, as well as your phone number, email, and your country's identification number. If this information is compromised, you could be in serious trouble. A malicious hacker could use your information to impersonate you and open a bank account in your name, apply for loans, or social assistance, make purchases, or use your identity to harass others online and commit crimes on your name. They could even extort you to gain some benefit. The loss of confidentiality of your information has personal, reputational, and economic consequences for you.
A common form of information theft is phishing, a cyberattack that you have already encountered. If you can't detect it, phishing has characteristics that you can identify if you pay attention.
Who can be the attacker behind the screen?
The malicious actor behind the screen can be a stranger, but even though it may be hard to believe, your attacker could also be an acquaintance, friend, or even a family member. Someone who knows you well enough and has motives to harm you could cyber-attack you. However, malicious hackers don't need to know you to benefit from you; they are experts at quickly obtaining valuable information that they can turn into money. Moreover, issues like revenge, envy, or unfair competition can lead a person to act against you even if they don't gain any economic benefit.
Perhaps you think you have no enemies or that your information is not relevant enough for someone to want it. You are a regular person who goes to university or works part-time, with normal friends you hang out with occasionally, and you have nothing interesting or attractive to an attacker. However, you would be surprised at the amount of data that comes out of you without you realizing it, and with which an attacker can profile you and gain some benefit. You don't need to be a highly influential person or have a lot of money for an attacker to target you. In fact, "ordinary" people are the easiest targets because they mistakenly believe that their information has no value. Don't you believe it? Consider these examples based on real cases.
Now let's look at some possible attack scenarios:
- Case 1:
Elena and Leticia are competing fiercely for the best average at the university, which depends on submitting a task online on the university's platform. It is known that the platform uses the students' email by default as a username to access the system and the national identification number as a password. Elena, who is very clever and knows this default information, obtains Leticia's data during breakfast at the cafeteria, accesses the university's platform with Leticia's identity, and deletes all her tasks. Elena achieves the best average by harming Leticia.
What happened?: Default access credentials should always be modified to avoid this type of situation. Leticia should have changed her password.
- Case 2:
Laura is buying a gift for her partner on a little-known online marketplace that she discovered through advertising on social networks at very attractive prices. When finalizing the purchase, Laura provides her address for shipping, tax information, and credit card details. According to the platform, the payment was processed successfully, and everything seems fine. Laura's credit card was cloned and used fraudulently. The attacker used her card to make unauthorized purchases for themselves.
What happened? - The online marketplace Laura was browsing was not legitimate; it was a fake website promoted to attract people and steal their data so that the attacker could make purchases on the name of the victims.
- Case 3:
Fernanda has just moved to a new city and is looking for friends through an application. She starts making friends with a guy who, before meeting her in person, asks her for money to solve a personal problem, promising prompt repayment. Immediately after that, Fernanda was blocked from the guy's profile. Fernanda fell victim to a social engineering attack.
What happened? - Social engineering is one of the attackers' favorite practices on the network. The guy Fernanda was chatting with was not real, but an attacker seeking money.
- Case 4:
Oscar has just acquired a new cellphone. While transferring all the information from his old device to the new one, Oscar forgets to set up a password and theft protection. Days later, he is mugged on the street, and the thief steals his device. Oscar receives constant phone calls and emails with threats to disclose his information if he does not make a payment to the criminal.
What happened? - Smartphones have multiple security filters and theft protection, and it should be one of the first configurations you do when you get a new device, in addition to taking measures with your app sessions and passwords. Oscar fell victim to extortion.
⚠️ All the people mentioned above were victims of a cyber attack, and this could happen to you too. These cases are very common, and you don't need to be a well-known person to be a victim.
Taking all of the above into a business context, imagine all the value of the massive information a company possesses and everything that can happen if this information falls into the wrong and unscrupulous hands of a cyber attacker. Even a dissatisfied candidate, employee, or former employee could perpetrate a cyber attack against the company or provide information to an attacker. Many times, cyber attacks start outside of computers.
What is a Cyber Attack?
A cyber attack is understood as any intentionally performed action that breaks one or more of the three pillars defended by cybersecurity. A cyber attack is a deliberate attempt to compromise the security of computer systems, networks, devices, or data to cause harm, steal confidential information, disrupt normal operations, or achieve some other malicious objective. Cyber attacks can be carried out by individuals, organized groups, or even nations and are executed using a variety of techniques and tools.
There are threats, incidents, and cyber attacks. Each has a different concept that should not be confused:
| Threat | Refers to the channel through which a cyber attack may be possible. An example of a threat would be having outdated software or an unprotected WiFi network. |
|---|---|
| Incident | Refers to a cyber accident that causes a disaster but was not intentionally executed. |
| Cyber Attack | Any action intentionally committed that compromises one or more of the three pillars of cybersecurity |