Introduction to Networks and Communications
Introduction to Networking: A Journey Through Connectivity
Networks have revolutionized the way the world communicates and shares information. These interconnected structures enable the transmission of data, resources, and services between electronic devices, regardless of their physical location. From the modest beginnings of electronic communication to the vast global networks that define the modern era, the evolution of networks has been a fascinating journey.
History of Networking: The First Steps
The history of networking dates back to the mid-20th century, when scientists began exploring ways to connect computers and share information. One of the key milestones in this evolution was the creation of ARPANET (Advanced Research Projects Agency Network) in the 1960s. ARPANET, funded by the U.S. Department of Defense, was the first network to use the packet-switched protocol, a method that divided data into smaller packets for transmission, resulting in greater efficiency and robustness compared to the circuit-switched methods used in traditional telephone networks.
ARPANET: The Beginnings of the Internet
ARPANET was established in 1969 and initially linked four universities in the United States: the University of California at Los Angeles (UCLA), Stanford Research Institute, the University of California at Santa Barbara, and the University of Utah. The first message transmitted over the ARPANET was "LOGIN," but the system crashed after only two letters, resulting in the first time "LO" was sent. Despite this modest beginning, ARPANET grew rapidly and laid the foundation for what would eventually become the Internet.
As the 1970s progressed, ARPANET continued to grow and more academic and research institutions joined the network. The creation of TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) in the 1980s was a crucial step in connecting different networks into an interconnected system. TCP/IP allowed different networks to communicate with each other, regardless of differences in their underlying technologies.
In 1983, the ARPANET officially adopted the TCP/IP protocol, marking the birth of the Internet as we know it today. As the technology evolved and became more accessible, the 1990s saw the popularization of the Internet worldwide, and the World Wide Web (WWW) became a graphical interface for accessing information online.
Computer network communications are based on the exchange of information between connected devices, such as computers, servers, mobile devices, and more. This exchange is achieved through the use of protocols and technologies that allow data to be transmitted and received efficiently and reliably.
-
Communication Protocols: Protocols are sets of rules and standards that define how devices on a network should communicate with each other. These protocols ensure that data is transmitted correctly and interpreted similarly at both ends of the communication. Examples of common protocols are TCP/IP, used on the Internet, and HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) for web browsing.
-
Data packetization: Information is divided into smaller packets before being sent over the network. Each packet contains a portion of the data as well as control information such as the source and destination address. This allows packets to be sent independently and reassembled at the final destination.
-
Routing and Switching: Devices in a network, such as routers and switches, are responsible for routing packets to their destination. Routers determine the most efficient route for packets to travel from one point to another on the network. Switches, on the other hand, manage the flow of data within a local network.
-
Client-Server Model: In many networks, the client-server model is used. Servers store and provide resources, such as web pages, files and services, to clients requesting those resources. Clients can be personal computers, mobile devices, or other connected devices.
💡 A network occurs when one device manages to connect to another and exchange information with it. This is not something that happens magically as there are several conditions for this communication to be possible. Before knowing those conditions, let's get to know the types of networks we may encounter in our first job!
- Local Area Networks (LAN): These are networks that cover a limited geographical area, such as an office, a building, or a house. LANs allow direct and fast communication between nearby devices.
- Wide Area Networks (WAN): These networks cover larger distances, such as cities, countries, or even continents. The Internet is an example of a global WAN.
- Metropolitan Area Networks (MAN): These networks are designed to cover metropolitan areas, such as a city. They provide greater coverage than a LAN, but not as extensive as a WAN.
- Wireless Networks: They use wireless transmission technologies, such as Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, to connect devices without the need for physical cables.
- Storage (SAN) networks: They are designed to share storage devices, such as hard disks and magnetic tapes, between servers.
- P2P (Peer-to-Peer) networks: In these networks, devices share resources directly with each other, without relying on a central server. It is common in file-sharing applications.
Network topologies
Network topologies refer to how devices are arranged and connected in a computer network. There are several common topologies, each with its advantages and disadvantages. Here is a clear explanation of each:
1. Star Topology:
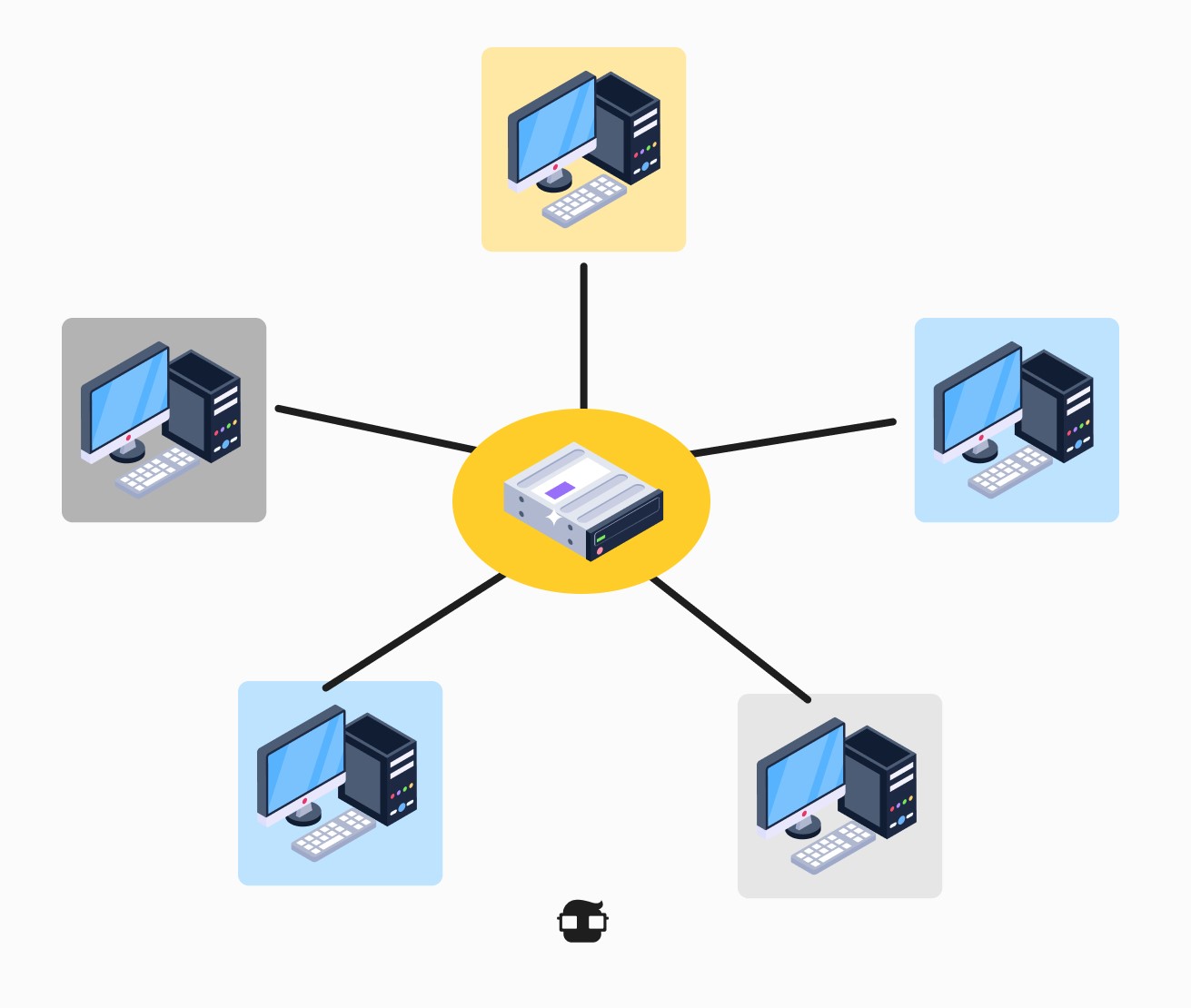
- Description: In this topology, all network devices are connected to a central point, such as a hub or switch. The devices are not directly connected; instead, they communicate through the central point.
- Advantages:
- Ease of adding or removing devices without disrupting the network.
- Failure of one device does not affect the others.
- Good performance in small and medium-sized networks.
- Disadvantages:
- If the central point fails, the entire network is affected.
- May require more cabling than other topologies.
2. Bus Topology:
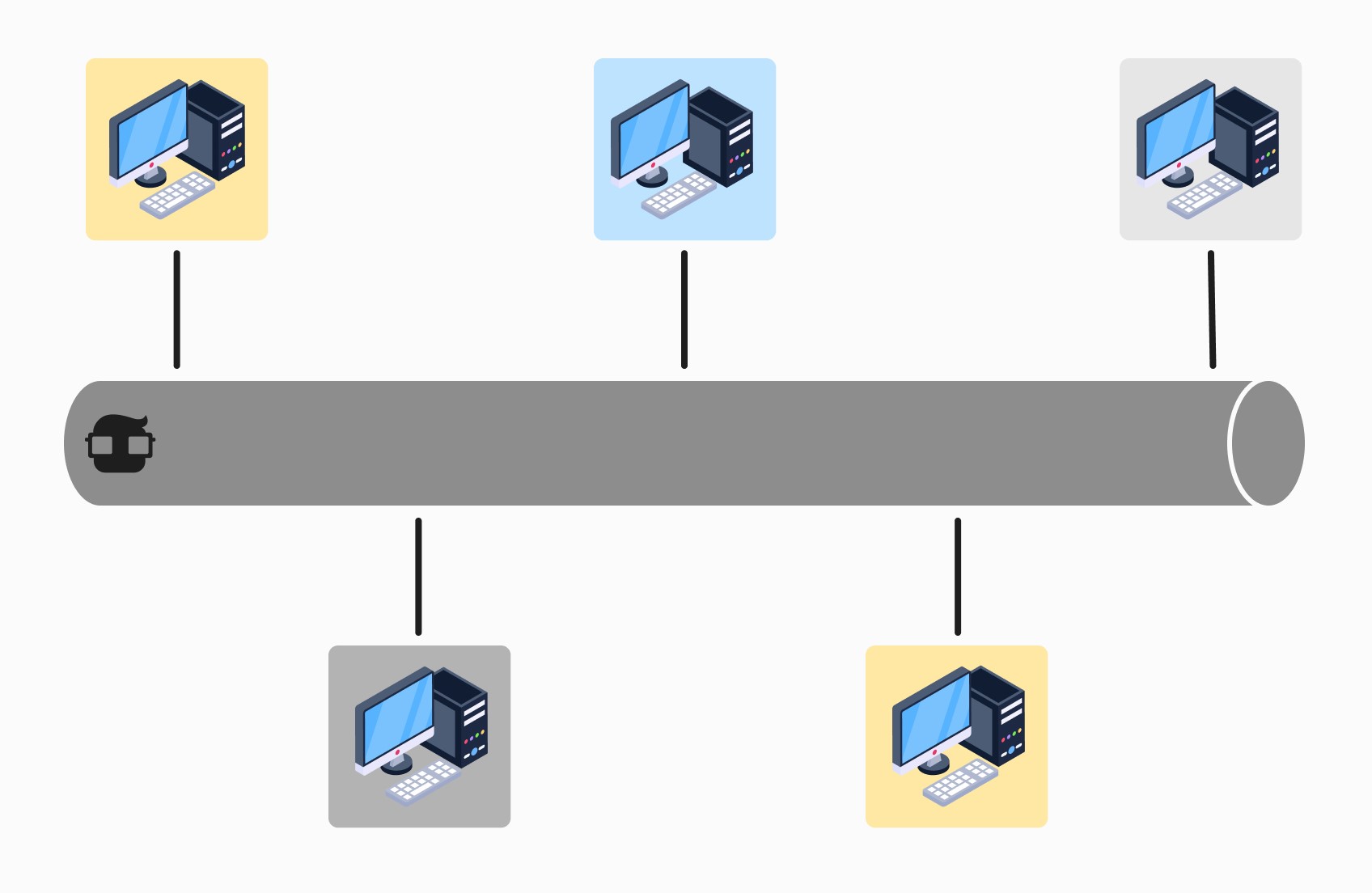
- Description: In this topology, all devices are connected to a single shared cable. Data is transmitted along this cable, and each device reads all data but only processes data destined for it.
- Advantages:
- Simple and easy to install.
- Good performance in small networks.
- Disadvantages:
- If the main cable breaks or fails, the entire network may stop working.
- Performance may degrade in large or congested networks.
Ring Topology:
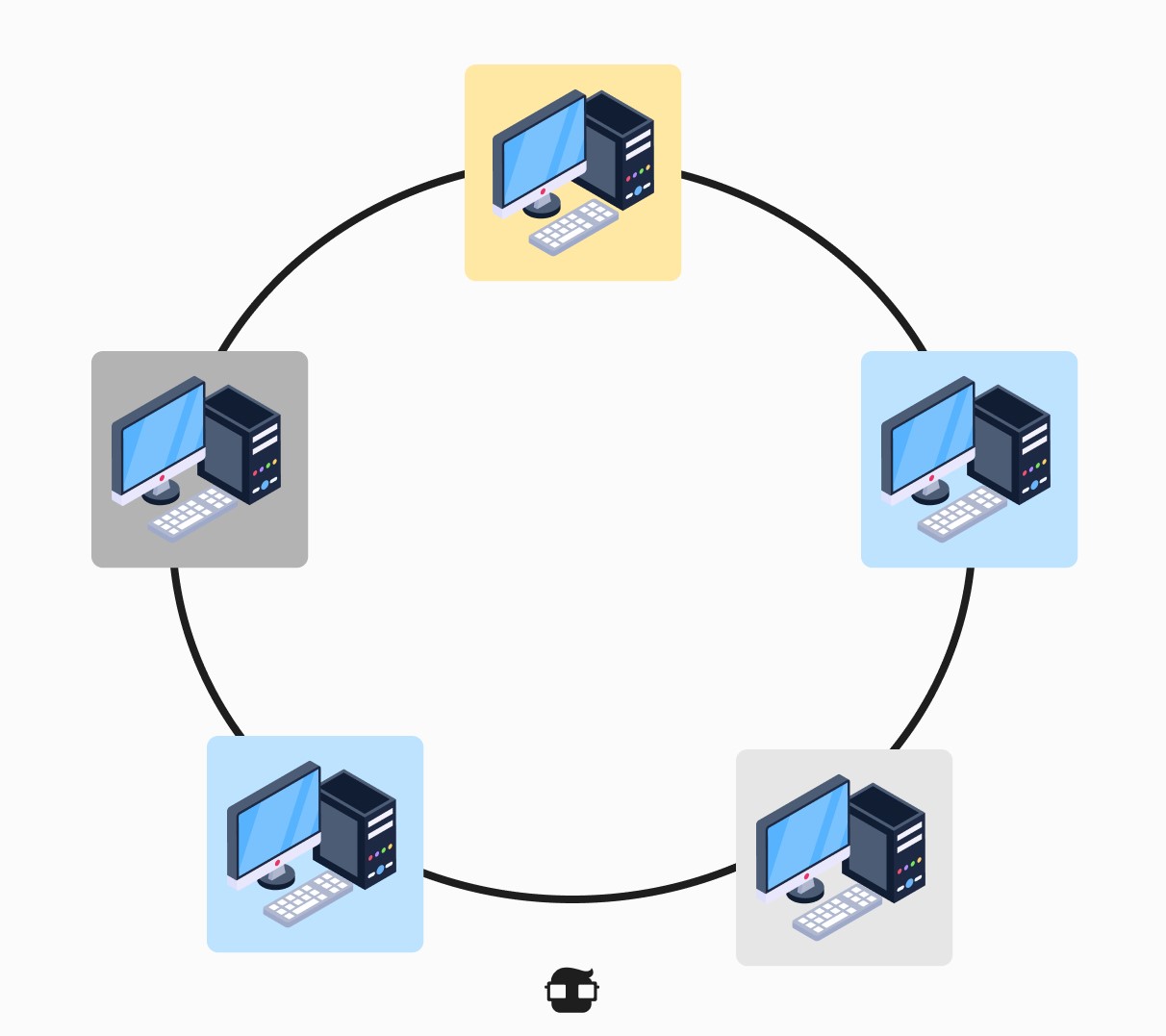
- Description: In this topology, devices are connected in a closed loop. Each device is connected to the next device, and the last device is connected to the first device. Data flows one-way through the ring until it reaches the destination device.
- Advantages:
- Good throughput and transmission speed.
- Each device has equal access to the network.
- Disadvantages:
- If one device or cable breaks down, it can affect the entire network.
- Less common than other topologies. 4. Mesh Topology:
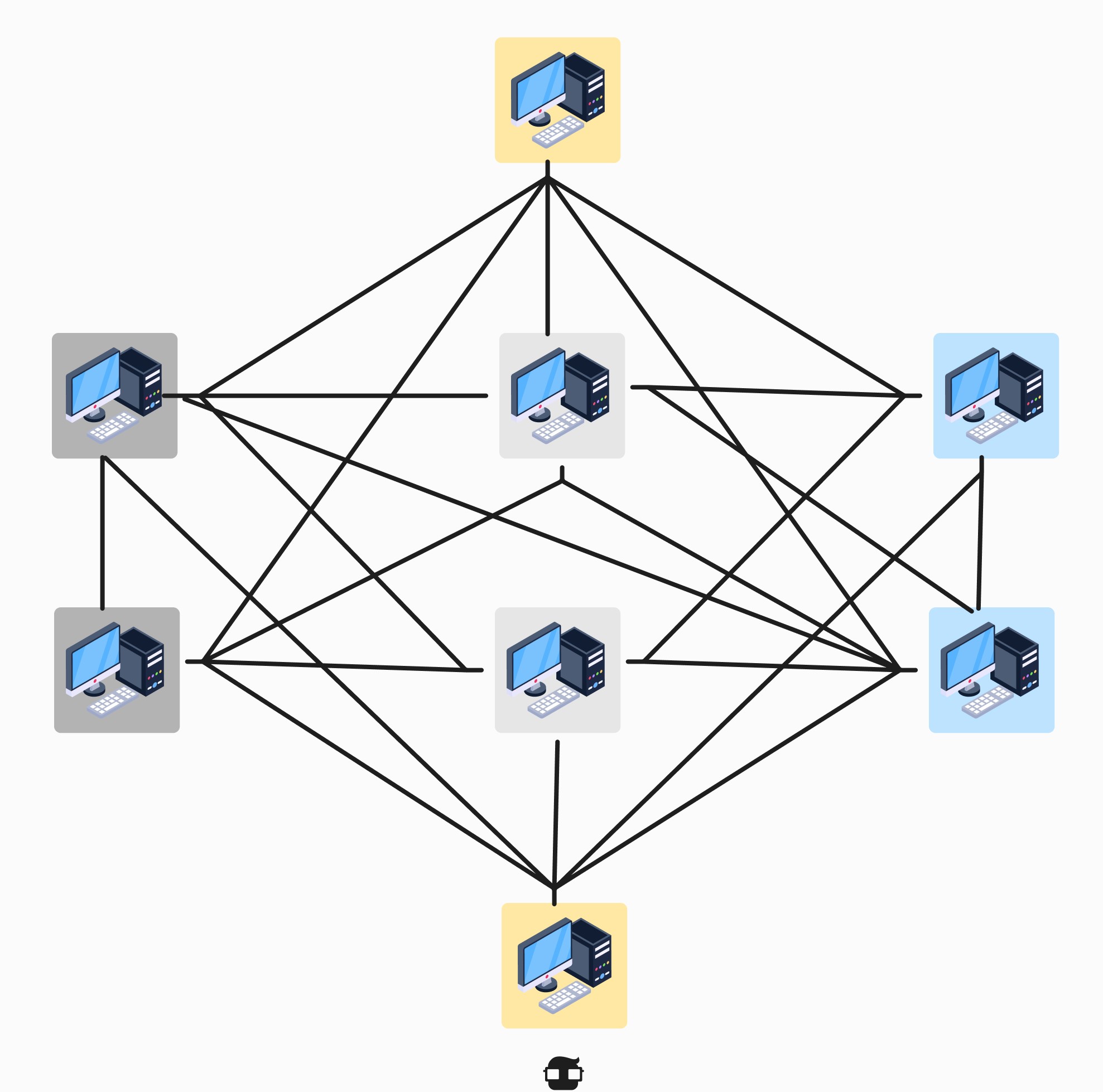
- Description: Each device is directly connected to all other devices in a mesh topology. This provides multiple paths for communication.
- Advantages:
- High redundancy and reliability, as failures on one link do not affect connectivity.
- Good for critical networks where reliability is paramount.
- Disadvantages:
- Requires a lot of cabling and can be costly to implement.
- Administration and maintenance can be complicated in large networks.
5. Tree Topology:
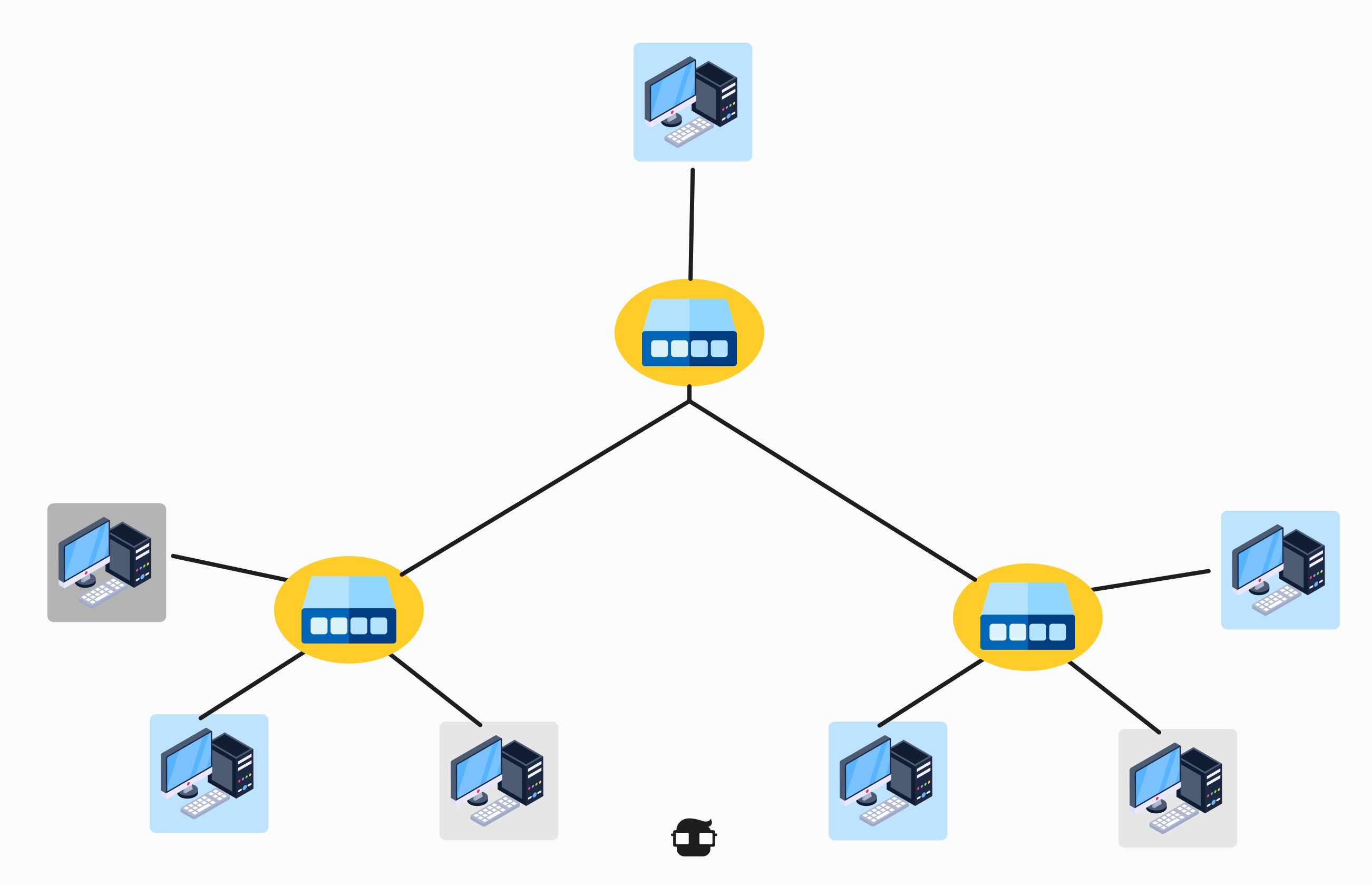
- Description: In this topology, devices are organized in a hierarchical tree-like structure, with a root node connecting to subnodes and so on.
- Advantages:
- Allows for easy network expansion.
- Provides some redundancy.
- Disadvantages:
- If the root node fails, it can affect the entire network.
- Not as robust as mesh topology in terms of redundancy.
Servers in Computer Networks: Power Behind Connectivity
Servers are essential components in a computer network. These powerful computers are designed to deliver services, resources, and data to other connected devices on the network. Servers play a critical role in the IT infrastructure of many organizations, enabling efficient communication, data storage, and shared resource management.
Types of Servers:
| File Server | Stores and manages files that can be accessed and shared by users and other devices on the network. This type of server is common in enterprise environments where documents and resources need to be shared centrally. |
|---|---|
| Web server | Hosts websites and web applications. It responds to requests from users' browsers and delivers web content, such as HTML pages, images, videos, and more. |
| Email Server | Manages email for an organization. Receives, stores, and sends email messages, allowing users to access their inboxes and send messages. |
| Database Server | Stores and manages databases containing structured information. It allows access, query, and manipulation of data by authorized applications and users. |
| Application Server | Runs business applications and provides application processing services for users and other systems on the network. |
| Proxy Server | Acts as an intermediary between devices on the local network and resources on the Internet. It can improve security and performance by caching content and filtering traffic. |
| DNS (Domain Name System) Server | Translates human-readable domain names into IP addresses that can be used by computers to locate resources on the network. |
| VPN (Virtual Private Network) Server | Provides secure connections over the Internet, allowing users to access network resources from remote locations as if they were on the local network. |
Role of Servers in an Enterprise Computer Network
In an enterprise computer network, servers play a crucial role in managing shared resources and services. Some key functions include:
- Centralization of Resources: Servers allow resources, such as files, applications, and databases, to be centralized and available to authorized users throughout the organization.
- User Management: Servers can implement security and authentication policies to ensure that only authorized users access network resources.
- Backup and Storage: File and storage servers enable backup and recovery of critical data, ensuring the integrity of business information.
- Internal and External Communications: E-mail and collaboration servers facilitate communication and collaboration among employees, as well as with external customers and partners.
- Web Publishing: Web servers enable companies to present their online presence and offer services and content via the World Wide Web.
- Application Management: Application servers enable the deployment and management of business applications critical to the operation of the organization.