GitHub
GitPod
Github Codespaces
How to use Github Codespaces
Modern companies no longer allow developers to work on their local computers; they use provisioning tools. Codespaces is GitHub's proposal for provisioning coding environments.
In plain English: Codespaces is a technology that creates, in a matter of seconds, computers and coding environments in the cloud, ready to be used by software developers.
In this lesson, we'll learn why Provisioning Environments are becoming a trend, their benefits and disadvantages, and how to use GitHub Codespaces.
Why code in the cloud instead of your local computer?
Coding in the cloud brings a lot of limitations, like requiring and relying on an internet connection, but the trend is clear: most companies will be using cloud environments in the next few years. But, Why?
Have you ever tried following an online tutorial, but after thoroughly following every step, the code still does not run on your computer?
Coding on your local computer also brings limitations: Local computers can break, and code can be lost. In addition, each local computer comes with different operating systems, Python versions, etc. Making sure your code is compatible to run on every computer can be challenging and unnecessary since it will get published on only one computer: The production environment.
Why Codespaces?
Codespaces is GitHub's proposal for provisioning coding environments. It dramatically simplifies the coding process, especially for new coders. With Codespaces, you can open any repository in a cloud coding environment and start or continue coding in seconds.
How do Codespaces work?
GitHub calls every coding environment a "codespace". If you start working on a project and create a new cloud computer to work on your project, this new computer will be called a "codespace".
💻 Every codespace is a virtual computer.
- Your list of current Codespaces (computers) is here: github.com/codespaces. (It's probably empty since you are just learning about it).
- The recommended way to create a new codespace is from a GitHub repository (if you need to learn what GitHub is, think of it as an online hard drive of code, where every folder is one of your coding projects).
-
Once the new codespace opens, it will create an empty computer for you, but it will also download the files from the GitHub repository folder you specified (your code) to this new computer.
-
Finally, it will open a coding editor (probably VSCode, the most used coding IDE in the world) and a terminal to start coding as if the codespace was on your local computer in the first place.
-
If you go back to your codespaces, you will find all the computers you have created and be able to re-open them. Changes you made to the files will stay for a few days; you will retain all data as long as you RE-OPEN the same workspace you were working on, or if you deactivate the "Auto-delete codespace" option on that specific codespace.
What is a GitHub Codespace?
It's a computer on the cloud, ready for you to start coding. You can go back to your list of Codespaces anytime and delete, rename, or pin each of the Codespaces.
When you open a GitHub repository using Codespaces, you will be "renting" a computer with access to the most popular coding editor in the world: VSCode.
Running a project on Codespaces
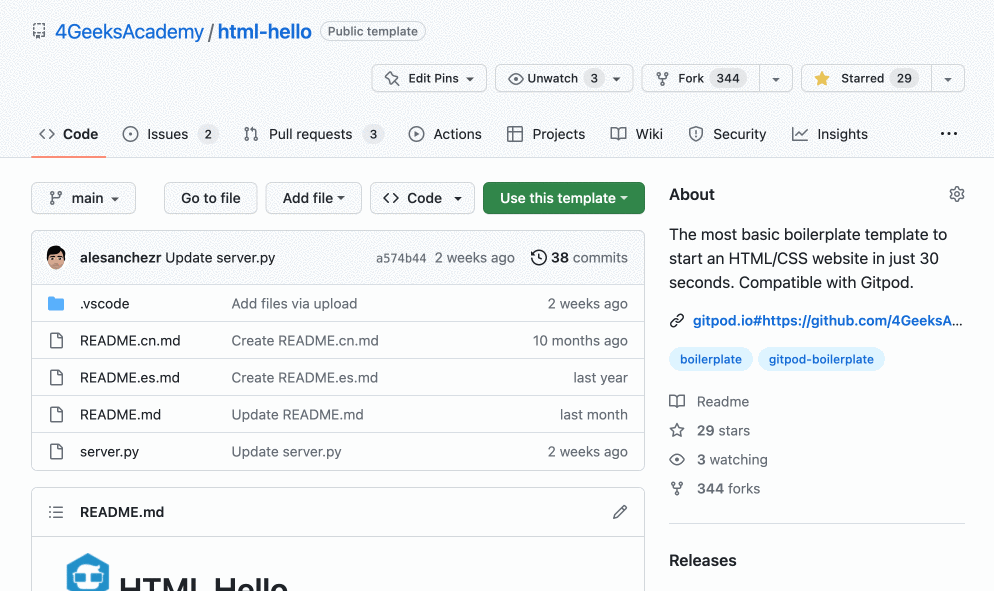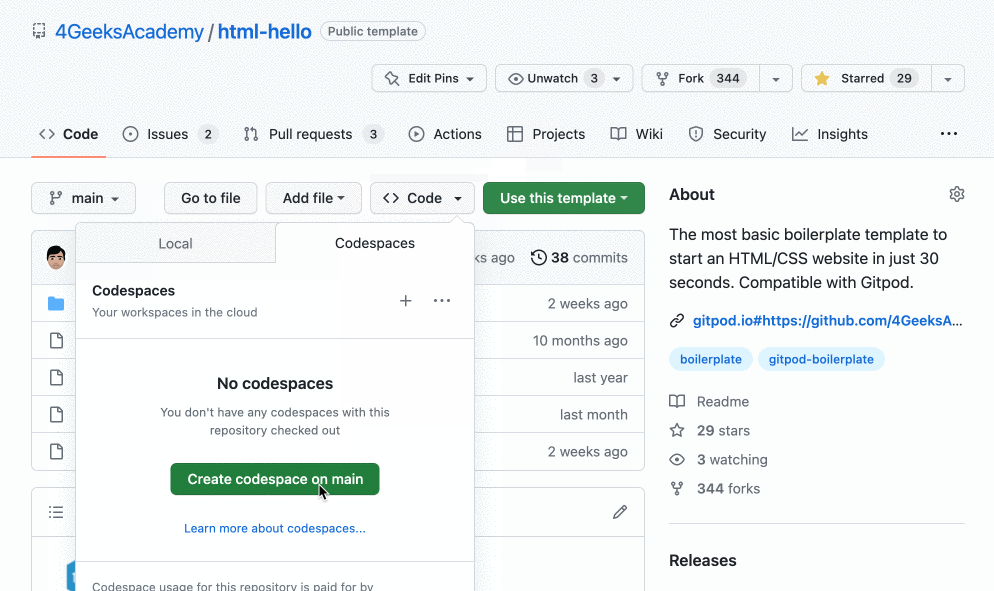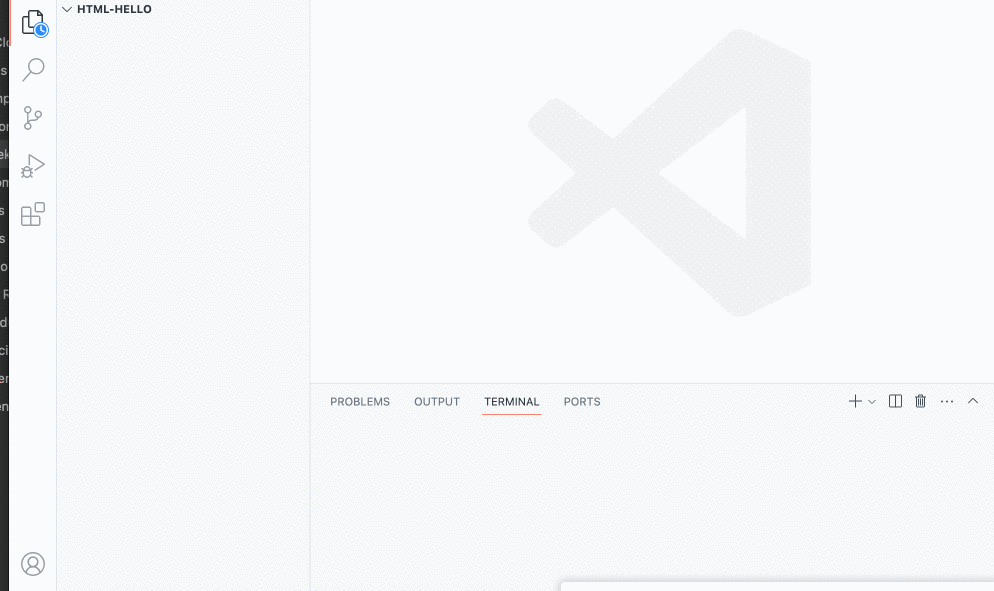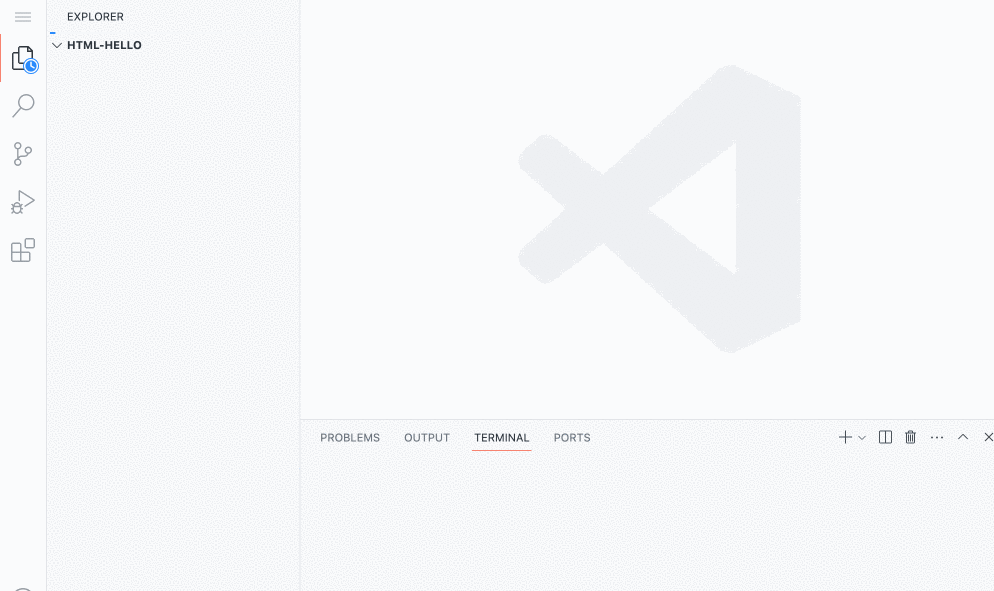
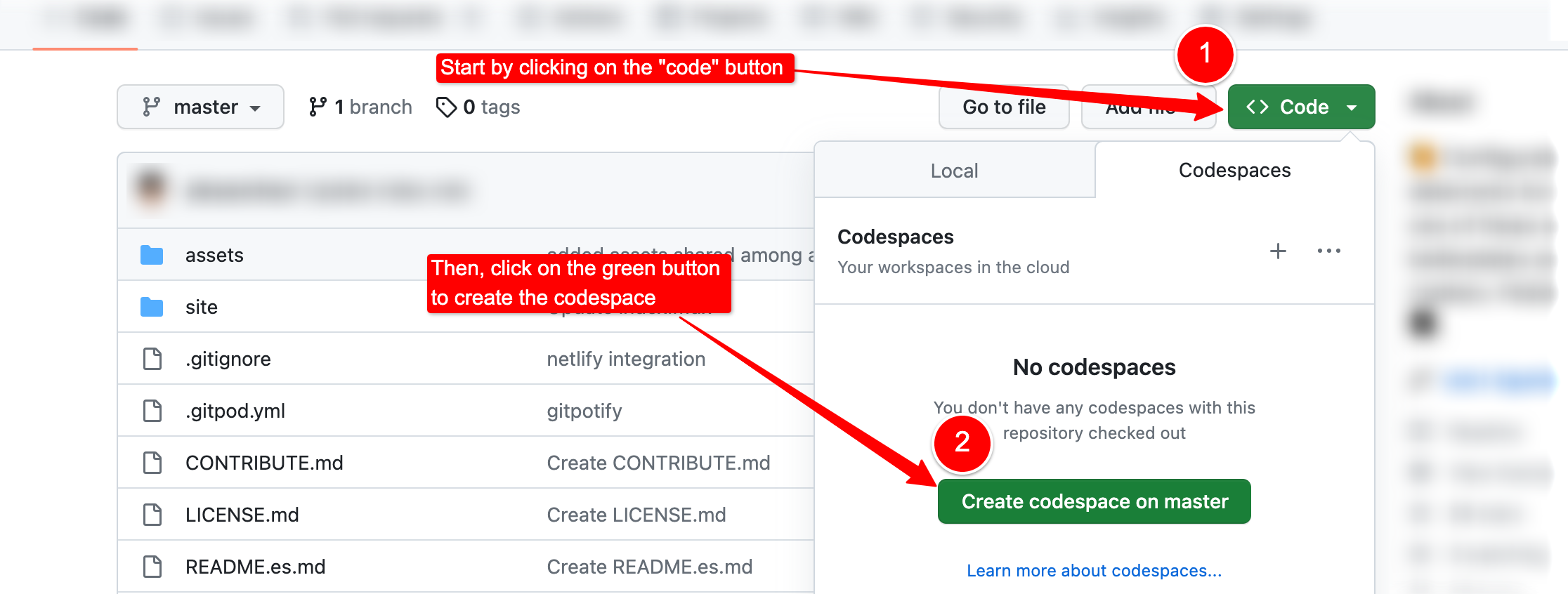
Go to any GitHub repository, and you will be able to open a codespace of it by clicking on the Code -> Create codespace on <branch> buttons. Look at this image:
The terminal
As a coder, you need to use the computer terminal sometimes; you can always find or open the terminal by clicking on the hamburger menu on the top left of VSCode and selecting the Terminal -> New Terminal option.

What is the terminal or command line?
Every computer has a terminal, and you can use it to do almost everything you want: open an application, create a file, folder, etc. However, in Codespaces, the terminal will only control the virtual computer.
You don't have to learn the terminal commands yet, but we strongly recommend reading this lesson to get familiar with them and understand their functions and limitations.