ENS Security Measures and Implementation
ENS Security Measures and Implementation
Before starting, we have thoroughly covered the ENS (Esquema Nacional de Seguridad) in several lessons. This lesson focuses solely on security measures and implementation. Read an Introduction to ENS and learn more about the Organizational and Operational Framework of ENS.
To implement Spain's National Security Framework (ENS) 🇪🇸, we first need to appoint a committee responsible for the scheme's implementation.

Key Roles Responsible for ENS Implementation within an Organization
Since the entry into force of Royal Decree 311/2022, the National Security Framework (ENS) clearly defines four key roles that must be present in all organizations subject to ENS compliance. These roles are specified in Article 11 of the decree and replace old models such as committees or presidents with casting votes, which are not included in the official regulations.
Each role has well-defined responsibilities to ensure the proper protection of systems, information, and services managed by an entity. Below are detailed descriptions:
🗂️ Information Owner
This role is responsible for determining the security requirements for the information processed within the system. This person, or a collegiate body, must identify the sensitivity and criticality of the data and establish the necessary protection levels according to Annex I of the ENS, which sets the system category.
Key responsibilities:
- Classify information.
- Identify risks associated with data processing.
- Establish security requirements based on sensitivity.
⚙️ Service Owner
Responsible for defining the security requirements of the services provided by the system. This involves assessing the impact of any alteration, interruption, or failure in service delivery and collaborating with the System Owner to identify risks and necessary measures.
Key responsibilities:
- Identify the impact of incidents on services.
- Set appropriate security levels for each service.
- Coordinate with the System Owner in planning measures.
🕵️♂️ Security Officer (CISO)
In charge of the comprehensive management of information security in the organization. Must develop security plans, conduct regular controls, coordinate audits, manage incidents, and serve as the point of contact with competent authorities.
Key responsibilities:
- Design, implement, and maintain security policies.
- Coordinate the Statement of Applicability (DoA).
- Oversee incident response and notify authorities.
- Lead training and awareness campaigns.
💻 System Owner
Mainly responsible for developing, operating, and maintaining the information system, ensuring that appropriate security measures are implemented and maintained throughout the system's lifecycle. Also responsible for categorizing the system according to the ENS and conducting risk analysis.
Key responsibilities:
- Define technical architecture and operational policies.
- Approve critical hardware/software configurations and changes.
- Keep risk analysis up to date.
- Coordinate with other owners to ensure service continuity and system protection.
🔒 Note: These four roles must be clearly defined, documented, and formally assigned within the organization and cannot be arbitrarily merged. Their proper implementation is a fundamental requirement for ENS compliance and obtaining the corresponding certification.
ENS Implementation: Phased Approach and Lifecycle
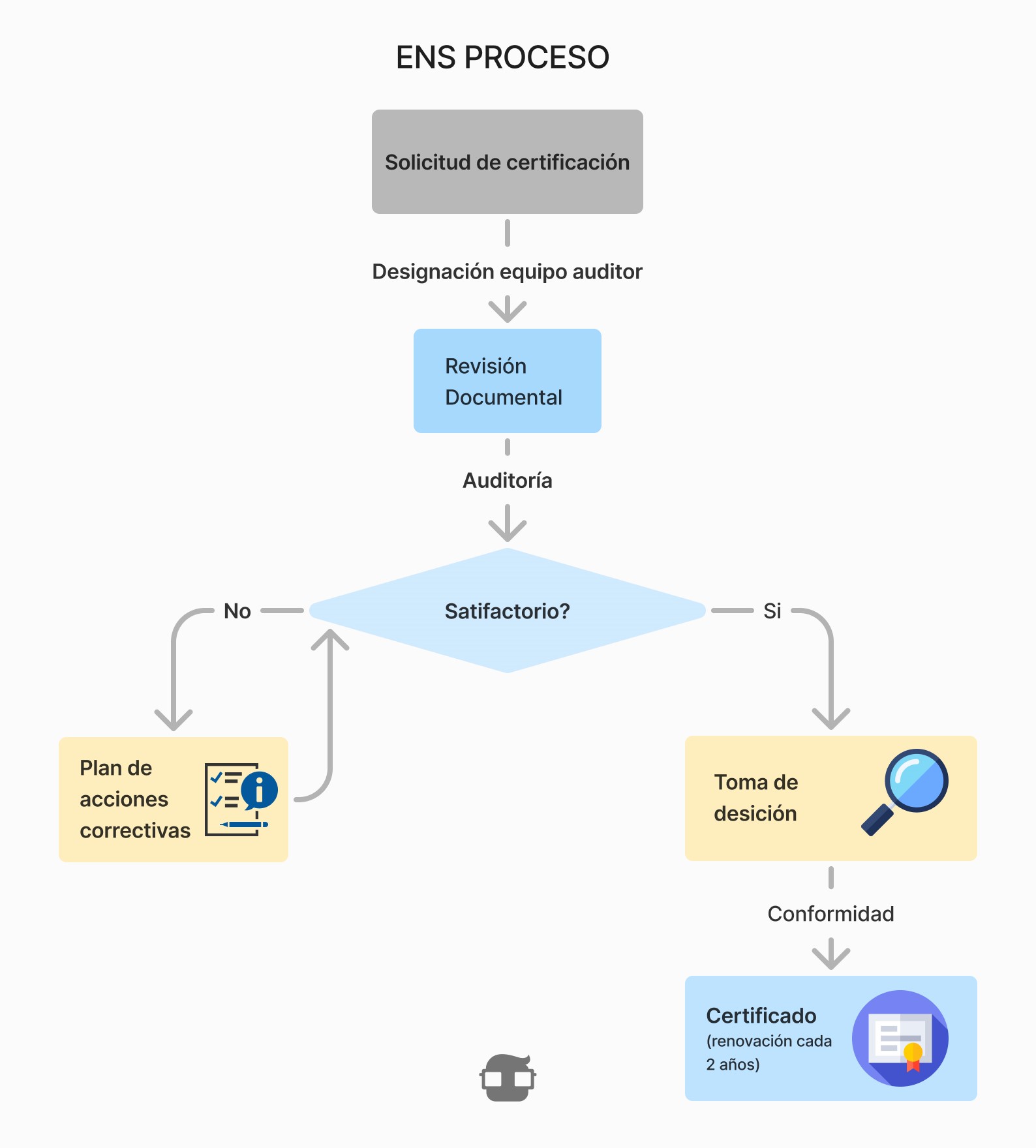
The implementation of the National Security Framework (ENS) should not be seen as a one-off action, but as a continuous process covering the entire system lifecycle, from initial design to final decommissioning.
This process must be guided by a risk analysis that determines which measures to apply, at what level of stringency (BASE, Reinforced, High), and at what stage. Proper ENS implementation ensures not only regulatory compliance but also effective protection of services and information.
1. Understanding the ENS
Before applying any measures, the organization must understand its context and obligations. This initial step lays the foundation for the rest of the process:
- Classify your systems: Determine if they are Low, Medium, or High level systems based on the impact a security breach would have on confidentiality, integrity, or availability.
- Review ENS Annexes I and II:
- Annex I: Establishes how to categorize systems by level.
- Annex II: Contains the 73 mandatory security measures, divided into organizational, operational, and protection measures.
- Assess current legal compliance: Ensure compliance with other complementary regulations, such as GDPR, LOPDGDD, Law 40/2015, or Law 39/2015, among others.
2. Gap Analysis
This analysis allows you to understand the organization's current state against ENS requirements and identify weaknesses:
- Compare ENS measures with the actual state of your systems.
- Identify which controls are not implemented or are insufficient.
- Classify each gap by impact and urgency.
This analysis will feed into the ENS Adaptation Plan, which outlines concrete steps to achieve compliance.
3. Security Governance
To comply with the ENS, the organization must establish a clear structure of responsibilities, without resorting to informal committees or bodies not recognized by regulations.
- Formally designate the four roles defined in Article 11 of RD 311/2022:
- Information Owner
- Service Owner
- System Owner
- Security Officer (CISO)
- Define functions, authority, approval flows, and coordination mechanisms among them.
4. Development of the ISMS (Information Security Management System)
This step involves creating the organizational and technical foundations for structured security management:
- Draft and implement security policies and procedures.
- Establish a risk management process, in line with recognized methodologies (such as MAGERIT).
- Classify information assets (data, services, infrastructure, personnel).
- Define protection controls according to their criticality.
5. Implementation of Technical Controls
Here, the ENS technical measures are deployed, always aligned with the risk analysis results. Among them:
- Data encryption (at rest and in transit).
- Robust authentication and access control mechanisms.
- Monitoring and incident detection systems.
- Backups, network segmentation, high availability, among others.
Technical implementation without clear governance or policies can be ineffective. Both components must go hand in hand.
6. Administrative Measures
Administrative measures complement technical and organizational ones, ensuring that the human factor is also properly managed:
- Security training and awareness programs for staff.
- Incident response protocols.
- Procedures for change management, configuration control, and periodic reviews.
7. Third-Party Relationships
Security does not end at the organization's boundaries. The ENS requires managing risks from external providers or contracted services:
- Review contracts and security clauses.
- Assess third-party risks.
- Supervise compliance with measures by providers (audits, reports, etc.).
8. Audit and Certification
Once measures are implemented, ENS compliance must be verified through audits:
- Obligated entities must undergo an external audit every 2 years.
- The audit must be conducted by an accredited body or independent unit, as established in Guide CCN-STIC 820.
- If the evaluation is passed, the ENS certificate is issued, valid for 24 months.
Certification is not the end, but the start of a continuous improvement cycle. Measures must be maintained and updated throughout the system's lifecycle.
ENS Security Measures
The security measures of the National Security Framework (ENS) are organized into three frameworks:
- Organizational framework (
org) - Operational framework (
op) - Protection measures (
mp)
Each measure has application levels according to the system's security profile:
=: BASE requirement (mandatory for all)+: Requirement for medium-level systems++: Requirement for high-level systems
This is not an exhaustive list. The full 73 measures are available in Guide CCN-STIC 808.
Organizational Framework (org)
Security Policies and Procedures
| Measure | Low Level | Medium Level | High Level | Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Security policies | = | + | ++ | org.2 |
| Security procedures | = | + | ++ | org.3 |
Authorization Processes
| Measure | Low Level | Medium Level | High Level | Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control of facilities and components | = | = | = | org.4 |
Operational Framework (op)
Planning
| Measure | Low Level | Medium Level | High Level | Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Risk analysis | = | + | ++ | op.pl.1 |
| Security architecture | = | + | ++ | op.pl.2 |
| Acquisition of new components | = | = | = | op.pl.3 |
| Capacity management | — | = | = | op.pl.4 |
Protection Measures (mp)
Facility Protection (mp.if.*)
| Measure | Low Level | Medium Level | High Level | Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Separate areas with access control | = | = | = | mp.if.1 |
| Identification of people | = | = | = | mp.if.2 |
| Conditioning of premises | = | = | = | mp.if.3 |
| Power supply | + | = | = | mp.if.4 |
| Fire protection | = | = | = | mp.if.5 |
| Flood protection | — | = | = | mp.if.6 |
| Equipment entry and exit log | = | = | = | mp.if.7 |
| Alternative facilities | — | — | = | mp.if.8 |
Personnel and Asset Protection (mp.per.*)
| Measure | Low Level | Medium Level | High Level | Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Job characterization | — | = | = | mp.per.1 |
| Duties and obligations | = | = | = | mp.per.2 |
| Awareness | = | = | = | mp.per.3 |
| Training | = | = | = | mp.per.4 |
| Alternative personnel | — | — | = | mp.per.5 |
| Alternative means (equipment) | — | — | = | mp.per.8 |
Information Protection (mp.info.*)
| Measure | Low Level | Medium Level | High Level | Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Personal data | = | = | = | mp.info.1 |
| Information classification | + | = | = | mp.info.2 |
| Encryption | — | — | = | mp.info.3 |
| Electronic signature | + | ++ | ++ | mp.info.4 |
| Timestamps | = | = | = | mp.info.5 |
| Document sanitization | = | = | = | mp.info.6 |
| Backups | = | = | = | mp.info.9 |
Service Protection (mp.s.*)
| Measure | Low Level | Medium Level | High Level | Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Email protection | = | = | = | mp.s.1 |
| Web services and application protection | = | + | + | mp.s.2 |
| Protection against denial of service | — | = | + | mp.s.8 |
| Alternative means for critical services | — | — | = | mp.s.9 |
Application Level Legend
=: BASE level, mandatory for all systems+: Applicable to medium-level systems++: Applicable to high-level systems—: Not explicitly applicable (may depend on risk analysis)