Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Machine Learning
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing
Cloud computing is a model for delivering technology services over the Internet. Instead of having to purchase and maintain in-house servers and hardware, businesses and/or users can access computing resources, such as servers, storage, databases, networks and software, through cloud service providers.
In essence, cloud computing allows organizations and individuals to use computing resources flexibly and on demand, paying only for what they actually use. This provides several advantages, such as:
- Scalability: Resources can be scaled up or down as needed, allowing for efficient use of resources and the ability to handle variable workloads.
- Remote access: Users can access their applications and data from anywhere with an Internet connection, facilitating collaboration and remote work.
- Reduced cost: By not requiring investment in physical infrastructure and hardware, organizations can avoid upfront costs and maintenance expenses. They only pay for the resources they consume.
- Simplified upgrades and maintenance: Cloud service providers take care of hardware and software management, freeing users from the burden of maintenance.
- Flexibility: They offer a variety of options and configurations to meet the specific needs of different users and businesses.
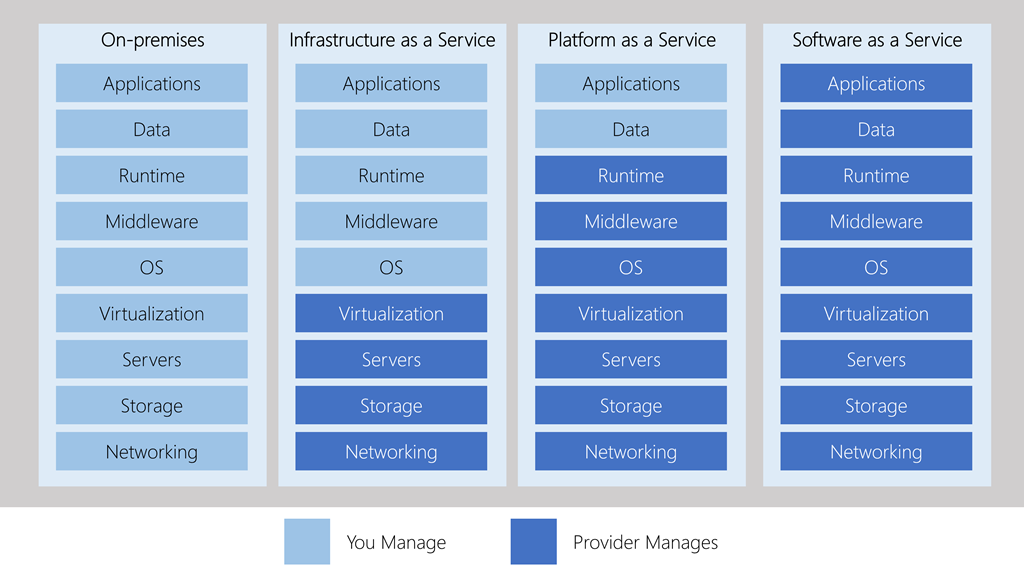
There are three main models of cloud services:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): provides access to basic infrastructure resources, such as virtual servers, storage and networking. In this type of service, we basically get a part of a giant computer(s) in the cloud. It's like renting just the hardware of a computer. Here, we are responsible for managing everything, such as installing operating systems and programs. It can be very flexible, as if we were building our own house and choosing every detail. Examples are services like Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): Provides a development and execution environment for developers to build, deploy and manage applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. This service is like being given a place in the cloud to build our house, but we already have some specific tools and materials ready to use. We can build applications using those tools without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. It's like someone giving us a construction kit to make our house instead of having to design each piece ourselves. Examples include Google App Engine and Heroku.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Delivers complete applications through the cloud. Users can access and use the software through a web browser without having to install or maintain it locally. With SaaS, we don't actually have to build anything. It's as if we already have a house fully furnished and ready to live in. We just need to move in and start living. Instead of installing programs on our computer, we access them through the Internet. For example, as with Gmail or Google Docs. We don't need to worry about the technical stuff, just use what's there.
| IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) | PaaS (Platform as a Service) | SaaS (Software as a Service) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Level of Abstraction | Low | Medium | High |
| Management Responsibility | User (Operating Systems, Networks) | Vendor (Platform, Middleware) | Vendor (Application) |
| Flexibility | High | Moderate | Low |
| Scalability | High | Moderate | Limited |
| Application Development | User Dependent | Platform Based | Not Required, Use Only |
| Examples | Virtual Machines (AWS, Azure) | Google App Engine, Heroku | Salesforce, Google Workspace |
Cloud computing, in terms of Machine Learning and, beyond that, Artificial Intelligence, is nowadays used in all its forms; from using third-party tools to develop models as fully integrated development environments in the cloud, through local developments and deployment in the cloud (the latter the most widely used).
Machine learning in the cloud
Although there is an infinite and very well distributed catalog of services to work in the field of machine learning, some of the most prominent and well-known are:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): AWS offers a wide range of services for machine learning, such as Amazon SageMaker, which is a comprehensive platform for building, training and deploying machine learning models. It also provides specific services such as Amazon Rekognition for image recognition and Amazon Polly for speech synthesis.
- Microsoft Azure: Azure Machine Learning is Microsoft's cloud machine learning offering. It provides tools and services to develop, train and deploy machine learning models. It also includes Azure Cognitive Services for natural language processing and computer vision capabilities.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP): Google Cloud offers Google Cloud AI Platform, which allows building, training and deploying machine learning models using TensorFlow and other popular frameworks. It also offers natural language processing services through the Cloud Natural Language API and image recognition through the Cloud Vision API.
- IBM Cloud: IBM offers IBM Watson, an artificial intelligence platform that encompasses machine learning and data analysis. Watson Studio is a tool for creating and training models, and Watson Machine Learning allows them to be implemented. They also offer natural language processing and text analytics services.
- Alibaba Cloud: Chinese vendor Alibaba Cloud offers machine learning services through the Alibaba Cloud Machine Learning Platform, which includes tools for building, training and deploying models. It also offers natural language processing and computer vision services.
- Oracle Cloud: Oracle Cloud provides machine learning and advanced analytics services through Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Data Science. It offers modeling, training and deployment capabilities, as well as integration with other Oracle tools.
Cloud data warehouses
Cloud data warehouses are systems designed to store large amounts of information in an efficient and scalable manner. With the recent increase in the size of data sets and the computing power needed to run machine learning models, leveraging cloud resources is a necessity for data science.
In data management, depending on how the data is stored, guarded and what the intended use is, there are different technologies available.
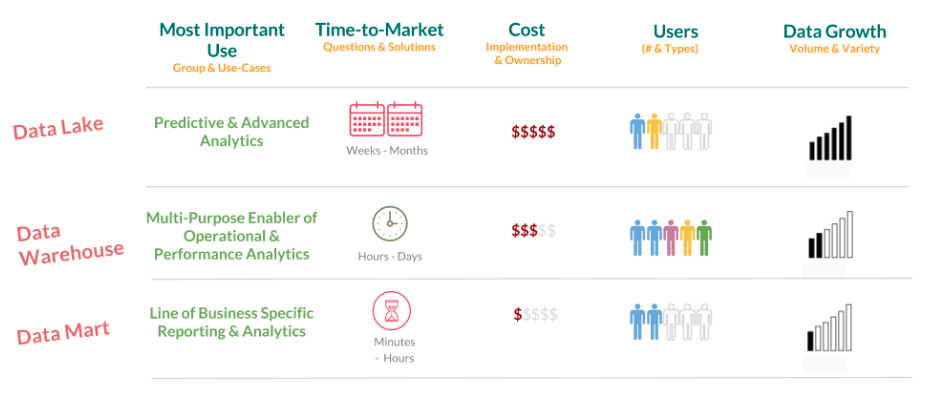
Data lake
A data lake is a repository that stores large volumes of data in its original, unprocessed format. This includes structured, semi-structured and unstructured data. The information is stored in its raw form, providing flexibility to analyze it in different contexts and extract valuable information.
This technology is especially useful for Big Data analysis and data exploration. Examples of technologies used in Data Lakes are Hadoop and cloud storage systems such as Amazon S3.
Data warehouse
A Data Warehouse is a centralized system that collects, organizes and stores data from different sources within an enterprise in a structured format optimized for analytical queries. The data in a Data Warehouse is usually historical and is designed to support decision making based on reporting and analysis. Data warehouses often use dimensional models and fact tables to enable complex queries. Examples of Data Warehouses include Amazon Redshift, Google BigQuery and Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics.
Data mart
A data mart is a smaller version of a Data Warehouse. It is designed to address the specific needs of a department or user group within an organization. Data Marts contain a portion of the Data Warehouse data and are optimized for a particular business area. They are useful for enabling users to access and analyze relevant data in a more efficient and targeted manner. Data Marts can be independent or extracted from the main Data Warehouse.
The main difference between a data lake and a data warehouse has to do with the format in which the data is processed and stored. In a data warehouse we will always find structured and preprocessed data, and in a data lake, we will not. Making the decision on which technology to implement will depend on the type of data we are working with and the frequency with which it will be updated. A data warehouse is a more analytical environment, and is not intended for frequent queries or updates.